The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Health Equity in Oncology: Scoping Review
- PMID: 36005841
- PMCID: PMC9667381
- DOI: 10.2196/39748
The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Health Equity in Oncology: Scoping Review
Abstract
Background: The field of oncology is at the forefront of advances in artificial intelligence (AI) in health care, providing an opportunity to examine the early integration of these technologies in clinical research and patient care. Hope that AI will revolutionize health care delivery and improve clinical outcomes has been accompanied by concerns about the impact of these technologies on health equity.
Objective: We aimed to conduct a scoping review of the literature to address the question, "What are the current and potential impacts of AI technologies on health equity in oncology?"
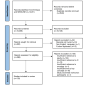
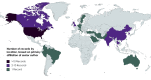
Methods: Following PRISMA-ScR (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews) guidelines for scoping reviews, we systematically searched MEDLINE and Embase electronic databases from January 2000 to August 2021 for records engaging with key concepts of AI, health equity, and oncology. We included all English-language articles that engaged with the 3 key concepts. Articles were analyzed qualitatively for themes pertaining to the influence of AI on health equity in oncology.
Results: Of the 14,011 records, 133 (0.95%) identified from our review were included. We identified 3 general themes in the literature: the use of AI to reduce health care disparities (58/133, 43.6%), concerns surrounding AI technologies and bias (16/133, 12.1%), and the use of AI to examine biological and social determinants of health (55/133, 41.4%). A total of 3% (4/133) of articles focused on many of these themes.
Conclusions: Our scoping review revealed 3 main themes on the impact of AI on health equity in oncology, which relate to AI's ability to help address health disparities, its potential to mitigate or exacerbate bias, and its capability to help elucidate determinants of health. Gaps in the literature included a lack of discussion of ethical challenges with the application of AI technologies in low- and middle-income countries, lack of discussion of problems of bias in AI algorithms, and a lack of justification for the use of AI technologies over traditional statistical methods to address specific research questions in oncology. Our review highlights a need to address these gaps to ensure a more equitable integration of AI in cancer research and clinical practice. The limitations of our study include its exploratory nature, its focus on oncology as opposed to all health care sectors, and its analysis of solely English-language articles.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; bias; cancer; cancer epidemiology; digital health; eHealth; epidemiology; global health; health disparity; health equity; machine learning; mobile phone; oncology; public health; review; scoping.
©Paul Istasy, Wen Shen Lee, Alla Iansavichene, Ross Upshur, Bishal Gyawali, Jacquelyn Burkell, Bekim Sadikovic, Alejandro Lazo-Langner, Benjamin Chin-Yee. Originally published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (https://www.jmir.org), 01.11.2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Bianchi P, Labory S. Industrial Policy for the Manufacturing Revolution. Cheltenham, United Kingdom: Edward Elgar Publishing; 2018. Jun 29, The fourth industrial revolution.
-
- Chin-Yee B, Upshur R. The impact of artificial intelligence on clinical judgment: a briefing document. AMS Healthcare. 2019. [2022-03-06]. https://www.ams-inc.on.ca/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/The-Impact-of-AI-on... .
-
- Chui M, Manyika J, Bughin J. Big Data's Potential for Businesses. McKinsey Global Institute. 2011. [2022-03-05]. https://www.mckinsey.com/mgi/overview/in-the-news/big-data-potential-for...
-
- Kann BH, Hosny A, Aerts HJ. Artificial intelligence for clinical oncology. Cancer Cell. 2021 Jul 12;39(7):916–27. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2021.04.002. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1535-6108(21)00210-5 S1535-6108(21)00210-5 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Luchini C, Pea A, Scarpa A. Artificial intelligence in oncology: current applications and future perspectives. Br J Cancer. 2022 Jan 26;126(1):4–9. doi: 10.1038/s41416-021-01633-1. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/34837074 10.1038/s41416-021-01633-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

