Relationship between Aggressiveness, Self-Confidence, and Perceived Coach Support and Head Impact Exposure in Youth Football
- PMID: 36006081
- PMCID: PMC9412463
- DOI: 10.3390/sports10080115
Relationship between Aggressiveness, Self-Confidence, and Perceived Coach Support and Head Impact Exposure in Youth Football
Abstract
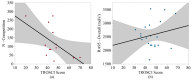
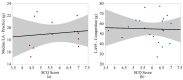
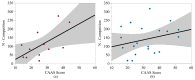
This study evaluated head impact exposure (HIE) metrics in relation to individual-level determinants of HIE. Youth (n = 13) and high school (n = 21) football players were instrumented with the Head Impact Telemetry (HIT) system during one season. Players completed the Trait-Robustness of Self-Confidence Inventory (TROSCI), Sports Climate Questionnaire (SCQ), and Competitive Aggressiveness and Anger Scale (CAAS), measuring self-confidence, perceived coach support, and competitive aggressiveness, respectively. Relationships between HIE metrics (number of impacts, median and 95th percentile accelerations, and risk-weighted exposure (RWE)) and survey scores were evaluated using linear regression analysis. For middle school athletes, TROSCI scores were significantly negatively associated with the number of competition impacts and the mean number of impacts per player per competition. SCQ scores were significantly positively associated with median linear acceleration during practice. CAAS scores were not significantly associated with biomechanical metrics at either level of play. Perceived coach support and self-confidence might influence HIE among middle school football players. Football athletes' competitive aggressiveness may have less influence their HIE than other factors.
Keywords: aggression; biomechanics; coach support; head acceleration; self-confidence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Stamm J.M., Koerte I.K., Muehlmann M., Pasternak O., Bourlas A.P., Baugh C.M., Giwerc M.Y., Zhu A., Coleman M.J., Bouix S., et al. Age at First Exposure to Football Is Associated with Altered Corpus Callosum White Matter Microstructure in Former Professional Football Players. J. Neurotrauma. 2015;32:1768–1776. doi: 10.1089/neu.2014.3822. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alosco M.L., Tripodis Y., Jarnagin J., Baugh C.M., Martin B., Chaisson C.E., Estochen N., Song L., Cantu R.C., Jeromin A., et al. Repetitive head impact exposure and later-life plasma total tau in former National Football League players. Alzheimer’s Dement. Diagn. Assess. Dis. Monit. 2016;7:33–40. doi: 10.1016/j.dadm.2016.11.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Montenigro P., Alosco M.L., Martin B.M., Daneshvar D., Mez J., Chaisson C.E., Nowinski C.J., Au R., McKee A.C., Cantu R.C., et al. Cumulative Head Impact Exposure Predicts Later-Life Depression, Apathy, Executive Dysfunction, and Cognitive Impairment in Former High School and College Football Players. J. Neurotrauma. 2017;34:328–340. doi: 10.1089/neu.2016.4413. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

