Effects of Two Antiretroviral Drugs on the Crustacean Daphnia magna in River Water
- PMID: 36006102
- PMCID: PMC9416331
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics10080423
Effects of Two Antiretroviral Drugs on the Crustacean Daphnia magna in River Water
Abstract
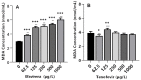
Antiretroviral (ARVs) drugs are used to manage the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) disease and are increasingly being detected in the aquatic environment. However, little is known about their effects on non-target aquatic organisms. Here, Daphnia magna neonates were exposed to Efavirenz (EFV) and Tenofovir (TFV) ARVs at 62.5-1000 µg/L for 48 h in river water. The endpoints assessed were mortality, immobilization, and biochemical biomarkers (catalase (CAT), glutathione S-transferase (GST), and malondialdehyde (MDA)). No mortality was observed over 48 h. Concentration- and time-dependent immobilization was observed for both ARVs only at 250-1000 µg/L after 48 h, with significant immobilization observed for EFV compared to TFV. Results for biochemical responses demonstrated that both ARVs induced significant changes in CAT and GST activities, and MDA levels, with effects higher for EFV compared to TFV. Biochemical responses were indicative of oxidative stress alterations. Hence, both ARVs could potentially be toxic to D. magna.
Keywords: Daphnia magna; Efavirenz; HIV antiretroviral drugs; Tenofovir; antioxidant enzymes; biochemical markers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Sublethal or not? Responses of multiple biomarkers in Daphnia magna to single and joint effects of BDE-47 and BDE-209.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2018 Nov 30;164:164-171. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.08.007. Epub 2018 Aug 11. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2018. PMID: 30107326
-
Response of biochemical biomarkers in the aquatic crustacean Daphnia magna exposed to silver nanoparticles.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2015 Dec;22(24):19990-9. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-5201-4. Epub 2015 Aug 23. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26296504
-
Gene response of CYP360A, CYP314, and GST and whole-organism changes in Daphnia magna exposed to ibuprofen.Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2016 Jan;179:49-56. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2015.08.010. Epub 2015 Sep 3. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26342857
-
Evaluation of boscalid toxicity on Daphnia magna by using antioxidant enzyme activities, the expression of genes related to antioxidant and detoxification systems, and life-history parameters.Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2020 Nov;237:108830. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2020.108830. Epub 2020 Jun 11. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32535132
-
Biochemical biomarkers in environmental studies--lessons learnt from enzymes catalase, glutathione S-transferase and cholinesterase in two crustacean species.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2010 Mar;17(3):571-81. doi: 10.1007/s11356-009-0112-x. Epub 2009 Mar 4. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2010. PMID: 19259718 Review.
Cited by
-
Toxic Effects of Methylene Blue on the Growth, Reproduction and Physiology of Daphnia magna.Toxics. 2023 Jul 7;11(7):594. doi: 10.3390/toxics11070594. Toxics. 2023. PMID: 37505561 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

