Spatial Distribution, Contamination Levels, and Health Risk Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Household Dust in Cairo City, Egypt
- PMID: 36006146
- PMCID: PMC9414935
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics10080466
Spatial Distribution, Contamination Levels, and Health Risk Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Household Dust in Cairo City, Egypt
Abstract
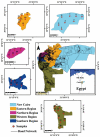
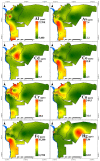
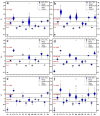
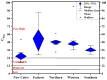
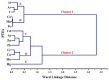
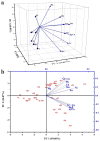
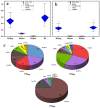
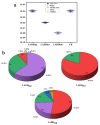
Urban areas’ pollution, which is owing to rapid urbanization and industrialization, is one of the most critical issues in densely populated cities such as Cairo. The concentrations and the spatial distribution of fourteen potentially toxic elements (PTEs) in household dust were investigated in Cairo City, Egypt. PTE exposure and human health risk were assessed using the USEPA’s exposure model and guidelines. The levels of As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg, Mo, Ni, Pb, and Zn surpassed the background values. Contamination factor index revealed that contamination levels are in the sequence Cd > Hg > Zn > Pb > Cu > As > Mo > Ni > Cr > Co > V > Mn > Fe > Al. The degree of contamination ranges from considerably to very high pollution. Elevated PTE concentrations in Cairo’s household dust may be due to heavy traffic emissions and industrial activities. The calculated noncarcinogenic risk for adults falls within the safe limit, while those for children exceed that limit in some sites. Cairo residents are at cancer risk owing to prolonged exposure to the indoor dust in their homes. A quick and targeted plan must be implemented to mitigate these risks.
Keywords: Cairo; exposure; indoor dust; pollution; potentially toxic elements; risk assessment; urban.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Alotaibi M.O., Albedair L.A., Alotaibi N.M., Elobeid M.M., Al-Swadi H.A., Alasmary Z., Ahmad M. Pollution Indexing and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy-Metals-Laden Indoor and Outdoor Dust in Elementary School Environments in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Atmosphere. 2022;13:464. doi: 10.3390/atmos13030464. - DOI
-
- Yehia M., Baghdady A., Howari F.M., Awad S., Gad A. Natural radioactivity and groundwater quality assessment in the northern area of the Western Desert of Egypt. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2017;12:331–344. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrh.2017.06.002. - DOI
-
- Farhat H.I. Impact of Drain Effluent on Surficial Sediments in the Mediterranean Coastal Wetland: Sedimentological Characteristics and Metal Pollution Status at Lake Manzala, Egypt. J. Ocean Univ. China. 2019;18:834–848. doi: 10.1007/s11802-019-3608-0. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

