HBM4EU Chromates Study-Genotoxicity and Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Workers Exposed to Hexavalent Chromium
- PMID: 36006162
- PMCID: PMC9412464
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics10080483
HBM4EU Chromates Study-Genotoxicity and Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Workers Exposed to Hexavalent Chromium
Abstract
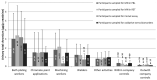
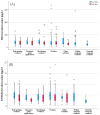
A study was conducted within the European Human Biomonitoring Initiative (HBM4EU) to characterize occupational exposure to Cr(VI). Herein we present the results of biomarkers of genotoxicity and oxidative stress, including micronucleus analysis in lymphocytes and reticulocytes, the comet assay in whole blood, and malondialdehyde and 8-oxo-2′-deoxyguanosine in urine. Workers from several Cr(VI)-related industrial activities and controls from industrial (within company) and non-industrial (outwith company) environments were included. The significantly increased genotoxicity (p = 0.03 for MN in lymphocytes and reticulocytes; p < 0.001 for comet assay data) and oxidative stress levels (p = 0.007 and p < 0.001 for MDA and 8-OHdG levels in pre-shift urine samples, respectively) that were detected in the exposed workers over the outwith company controls suggest that Cr(VI) exposure might still represent a health risk, particularly, for chrome painters and electrolytic bath platers, despite the low Cr exposure. The within-company controls displayed DNA and chromosomal damage levels that were comparable to those of the exposed group, highlighting the relevance of considering all industry workers as potentially exposed. The use of effect biomarkers proved their capacity to detect the early biological effects from low Cr(VI) exposure, and to contribute to identifying subgroups that are at higher risk. Overall, this study reinforces the need for further re-evaluation of the occupational exposure limit and better application of protection measures. However, it also raised some additional questions and unexplained inconsistencies that need follow-up studies to be clarified.
Keywords: 8-OHdG; MDA; biomonitoring; chromate; comet assay; effect biomarkers; micronuclei; occupational exposure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The SAM-Krom biomonitoring study shows occupational exposure to hexavalent chromium and increased genotoxicity in Denmark.Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2025 Mar;264:114444. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheh.2024.114444. Epub 2024 Sep 23. Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2025. PMID: 39317609
-
HBM4EU chromates study: the Portuguese integrated and harmonized study on exposure to hexavalent chromium and related early effects.Ann Work Expo Health. 2025 Feb 25;69(2):147-159. doi: 10.1093/annweh/wxae091. Ann Work Expo Health. 2025. PMID: 39657029
-
HBM4EU chromates study - Usefulness of measurement of blood chromium levels in the assessment of occupational Cr(VI) exposure.Environ Res. 2022 Nov;214(Pt 1):113758. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.113758. Epub 2022 Jun 25. Environ Res. 2022. PMID: 35764127
-
The HBM4EU chromates study - Outcomes and impacts on EU policies and occupational health practices.Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2023 Mar;248:114099. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheh.2022.114099. Epub 2022 Dec 17. Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2023. PMID: 36528954 Review.
-
Implementation of effect biomarkers in human biomonitoring studies: A systematic approach synergizing toxicological and epidemiological knowledge.Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2023 Apr;249:114140. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheh.2023.114140. Epub 2023 Feb 24. Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2023. PMID: 36841007 Review.
Cited by
-
Particulate hexavalent chromium inhibits global transcription of genes in DNA repair pathways, particularly targeting homologous recombination repair, base excision repair, mismatch repair and microhomology-mediated end-joining.J Hazard Mater. 2025 Mar 5;485:136892. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.136892. Epub 2024 Dec 15. J Hazard Mater. 2025. PMID: 39706010
-
Carcinogenic Mechanisms of Hexavalent Chromium: From DNA Breaks to Chromosome Instability and Neoplastic Transformation.Curr Environ Health Rep. 2024 Dec;11(4):484-546. doi: 10.1007/s40572-024-00460-9. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Curr Environ Health Rep. 2024. PMID: 39466546 Review.
-
Prolonged Particulate Hexavalent Chromium Exposure Induces DNA Double-Strand Breaks and Inhibits Homologous Recombination Repair in Primary Rodent Lung Cells.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2024 Dec;202(12):5653-5663. doi: 10.1007/s12011-024-04136-1. Epub 2024 Mar 18. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2024. PMID: 38499919
-
Serum Phthalate Concentrations and Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress in Adipose Tissue in a Spanish Adult Cohort.Environ Sci Technol. 2024 May 7;58(18):7719-7730. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.3c07150. Epub 2024 Apr 23. Environ Sci Technol. 2024. PMID: 38651840 Free PMC article.
-
Prolonged particulate hexavalent chromium exposure induces RAD51 foci inhibition and cytoplasmic accumulation in immortalized and primary human lung bronchial epithelial cells.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2023 Nov 15;479:116711. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2023.116711. Epub 2023 Oct 5. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37805091 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Recommendation from the Scientific Committee on Occupational Exposure Limits. European Commission; Brussels, Belgium: 2017. SCOEL/REC/386 Chromiun VI compounds. - DOI
-
- IARC . IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. IARCPress; Lyon, France: 2018. Chromium (VI) compounds; pp. 147–167.
-
- Ventura C., Gomes B.C., Oberemm A., Louro H., Huuskonen P., Mustieles V., Fernández M.F., Ndaw S., Mengelers M., Luijten M., et al. Biomarkers of effect as determined in human biomonitoring studies on hexavalent chromium and cadmium in the period 2008–2020. Environ. Res. 2021;197:110998. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.110998. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

