Nivalenol Mycotoxin Concerns in Foods: An Overview on Occurrence, Impact on Human and Animal Health and Its Detection and Management Strategies
- PMID: 36006189
- PMCID: PMC9413460
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins14080527
Nivalenol Mycotoxin Concerns in Foods: An Overview on Occurrence, Impact on Human and Animal Health and Its Detection and Management Strategies
Abstract
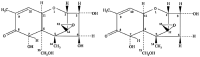
Mycotoxins are secondary metabolites produced by fungi that infect a wide range of foods worldwide. Nivalenol (NIV), a type B trichothecene produced by numerous Fusarium species, has the ability to infect a variety of foods both in the field and during post-harvest handling and management. NIV is frequently found in cereal and cereal-based goods, and its strong cytotoxicity poses major concerns for both human and animal health. To address these issues, this review briefly overviews the sources, occurrence, chemistry and biosynthesis of NIV. Additionally, a brief overview of several sophisticated detection and management techniques is included, along with the implications of processing and environmental factors on the formation of NIV. This review's main goal is to offer trustworthy and current information on NIV as a mycotoxin concern in foods, with potential mitigation measures to assure food safety and security.
Keywords: detection and management strategies; food contamination; human and animal health; nivalenol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Type B Trichothecenes in Cereal Grains and Their Products: Recent Advances on Occurrence, Toxicology, Analysis and Post-Harvest Decontamination Strategies.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Jan 17;15(2):85. doi: 10.3390/toxins15020085. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36828399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fusarial toxins: secondary metabolites of Fusarium fungi.Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2014;228:101-20. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-01619-1_5. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 24162094 Review.
-
Occurrence, mitigation and in vitro cytotoxicity of nivalenol, a type B trichothecene mycotoxin - Updates from the last decade (2010-2020).Food Chem Toxicol. 2021 Jun;152:112182. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2021.112182. Epub 2021 Apr 8. Food Chem Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33838177 Review.
-
Fusarium cerealis causing Fusarium head blight of durum wheat and its associated mycotoxins.Int J Food Microbiol. 2021 May 16;346:109161. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2021.109161. Epub 2021 Mar 17. Int J Food Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33773354
-
A survey of the natural occurrence of Fusarium mycotoxins in cereals grown in New Zealand in 1986-1989.Food Addit Contam. 1991 Sep-Oct;8(5):599-605. doi: 10.1080/02652039109374013. Food Addit Contam. 1991. PMID: 1840181
Cited by
-
Comparative Enzymatic and Gene Expression Responses in Wheat to DON- and NIV-Producing Fusarium Species.Biology (Basel). 2025 Aug 16;14(8):1063. doi: 10.3390/biology14081063. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40906366 Free PMC article.
-
Substance P and Glucagon-like Peptide-17-36 Amide Mediate Anorexic Responses to Trichothecene Deoxynivalenol and Its Congeners.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Dec 18;14(12):885. doi: 10.3390/toxins14120885. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36548782 Free PMC article.
-
Fusarium Head Blight in Argentina, a Profile of Produced Mycotoxins and a Biocontrol Strategy in Barley During Micro-Malting Process.Toxins (Basel). 2025 Jan 15;17(1):39. doi: 10.3390/toxins17010039. Toxins (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39852992 Free PMC article.
-
Type B Trichothecenes in Cereal Grains and Their Products: Recent Advances on Occurrence, Toxicology, Analysis and Post-Harvest Decontamination Strategies.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Jan 17;15(2):85. doi: 10.3390/toxins15020085. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36828399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aflatoxins in Cereals and Cereal-Based Products: Occurrence, Toxicity, Impact on Human Health, and Their Detoxification and Management Strategies.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Oct 6;14(10):687. doi: 10.3390/toxins14100687. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36287956 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mahato D.K., Devi S., Pandhi S., Sharma B., Maurya K.K., Mishra S., Dhawan K., Selvakumar R., Kamle M., Mishra A.K. Occurrence, impact on agriculture, human health, and management strategies of zearalenone in food and feed: A review. Toxins. 2021;13:92. doi: 10.3390/toxins13020092. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources