Preparation of Monoclonal Antibody against Deoxynivalenol and Development of Immunoassays
- PMID: 36006195
- PMCID: PMC9415657
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins14080533
Preparation of Monoclonal Antibody against Deoxynivalenol and Development of Immunoassays
Abstract
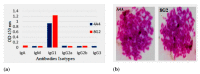
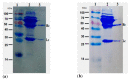
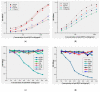
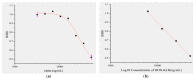
Fusarium toxins are the largest group of mycotoxins, which contain more than 140 known secondary metabolites of fungi. Deoxynivalenol (DON) is one of the most important compounds of this class due to its high toxicity and its potential to harm mankind and animals and a widespread contaminant of agricultural commodities, such as wheat, corn, barley, oats, bread, and biscuits. Herein, a hybridoma cell 8G2 secreting mAb against DON was produced by fusing the splenocytes with a tumor cell line Sp2/0. The obtained mAb had a high affinity (2.39 × 109 L/mol) to DON. An indirect competitive Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ic-ELISA) showed that the linear range for DON detection was 3.125-25 μg/mL, and the minimum inhibitory concentration (IC50) was 18.125 μg/mL with a limit of detection (LOD) of 7.875 μg/mL. A colloidal gold nanoparticle (AuNP) with 20 nm in diameter was synthesized for on-site detection of DON within 10 min with vLOD of 20 μg/mL. To improve the limit of detection, the gold nanoflower (AuNF) with a larger size (75 nm) was used to develop the AuNF-based strip with vLOD of 6.67 μg/mL. Compared to the vLOD of a convectional AuNP-based strip, the AuNF-based strip was three times lower. Herein, three immunoassay methods (ic-ELISA and AuNP/AuNF-based strips) were successfully developed, and these methods could be applied for the DON detection in agricultural products.
Keywords: ELISA; cell fusion; deoxynivalenol; immunochromatographic strips; monoclonal antibody.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Development of ELISA and Lateral Flow Immunoassays for Ochratoxins (OTA and OTB) Detection Based on Monoclonal Antibody.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Mar 6;10:80. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00080. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32211342 Free PMC article.
-
High-sensitivity and rapid immunoassays for furosine detection based on monoclonal antibody 1C3.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 May;309(Pt 4):143126. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.143126. Epub 2025 Apr 12. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 40228771
-
Preparation of monoclonal antibody against penicillic acid (PA) and its application in the immunological detection.Food Chem. 2020 Jul 30;319:126505. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126505. Epub 2020 Feb 27. Food Chem. 2020. PMID: 32169762
-
A peptide/maltose-binding protein fusion protein used to replace the traditional antigen for immunological detection of deoxynivalenol in food and feed.Food Chem. 2018 Dec 1;268:242-248. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.06.096. Epub 2018 Jun 20. Food Chem. 2018. PMID: 30064753
-
Development of immunoassay methods based on monoclonal antibody and its application in the determination of cadmium ion.J Hazard Mater. 2021 Jun 5;411:124992. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124992. Epub 2020 Dec 31. J Hazard Mater. 2021. PMID: 33454572
Cited by
-
Comparison of Synthetic Methods and Identification of Several Artificial Antigens of Deoxynivalenol.Molecules. 2023 Mar 20;28(6):2789. doi: 10.3390/molecules28062789. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36985761 Free PMC article.
-
Development of alkaline phosphatase-linked single-chain variable fragment fusion proteins for one-step immunodetection of deoxynivalenol in cereals.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2024 May;416(12):2929-2939. doi: 10.1007/s00216-024-05241-9. Epub 2024 Mar 16. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2024. PMID: 38491149
References
-
- Zuo H.G., Zhu J.X., Shi L., Zhan C.R., Guo P., Wang Y., Zhang Y., Liu J. Development of a novel immunoaffinity column for the determination of deoxynivalenol and its acetylated derivatives in cereals. Food Anal. Methods. 2018;11:2252–2260. doi: 10.1007/s12161-018-1211-4. - DOI
-
- Deng C., Li C., Zhou S., Wang X., Xu H., Wang D., Gong Y.Y., Routledge M.N., Zhao Y., Wu Y. Risk assessment of deoxynivalenol in high-risk area of China by human biomonitoring using an improved high throughput UPLC-MS/MS method. Sci. Rep. 2018;8:3901. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22206-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

