Analysis of Total-Forms of Cyanotoxins Microcystins in Biological Matrices: A Methodological Review
- PMID: 36006212
- PMCID: PMC9416067
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins14080550
Analysis of Total-Forms of Cyanotoxins Microcystins in Biological Matrices: A Methodological Review
Abstract
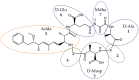
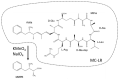
Microcystins (MCs) are cyclic heptapeptidic toxins produced by many cyanobacteria. Microcystins can be accumulated in various matrices in two forms: a free cellular fraction and a covalently protein-bound form. To detect and quantify the concentration of microcystins, a panel of techniques on various matrices (water, sediments, and animal tissues) is available. The analysis of MCs can concern the free or the total (free plus covalently bound) fractions. Free-form analyses of MCs are the most common and easiest to detect, whereas total-form analyses are much less frequent and more complex to achieve. The objective of this review is to summarize the different methods of extraction and analysis that have been developed for total forms. Four extraction methods were identified: MMPB (2-methyl-3-methoxy-4-phenylbutyric acid) method, deconjugation at basic pH, ozonolysis, and laser irradiation desorption. The study of the bibliography on the methods of extraction and analysis of the total forms of MCs showed that the reference method for the subject remains the MMPB method even if alternative methods and, in particular, deconjugation at basic pH, showed results encouraging the continuation of the methodological development on different matrices and on naturally-contaminated samples.
Keywords: MMPB method; cyanotoxins; deconjugation at basic pH; laser irradiation desorption; method of analysis; microcystins; ozonolysis; total toxins content.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Analysis of total microcystins by Lemieux oxidation and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry in fish and mussels tissues: Optimization and comparison of protocols.Sci Total Environ. 2024 Nov 10;950:175339. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.175339. Epub 2024 Aug 6. Sci Total Environ. 2024. PMID: 39117191
-
Transformation of microcystins to 2-methyl-3-methoxy-4-phenylbutyric acid by room temperature ozone oxidation for rapid quantification of total microcystins.Environ Sci Process Impacts. 2016 Apr;18(4):493-9. doi: 10.1039/c5em00588d. Epub 2016 Mar 15. Environ Sci Process Impacts. 2016. PMID: 26975781
-
Total microcystins analysis in water using laser diode thermal desorption-atmospheric pressure chemical ionization-tandem mass spectrometry.Anal Chim Acta. 2014 Apr 11;820:76-83. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2014.02.021. Epub 2014 Feb 19. Anal Chim Acta. 2014. PMID: 24745740
-
Recent developments in the methods of quantitative analysis of microcystins.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2020 Dec;34(12):e22582. doi: 10.1002/jbt.22582. Epub 2020 Jul 14. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 32662914 Review.
-
An overview of the accumulation of microcystins in aquatic ecosystems.J Environ Manage. 2018 May 1;213:520-529. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.01.077. Epub 2018 Feb 19. J Environ Manage. 2018. PMID: 29472035 Review.
Cited by
-
Health and Environmental Impacts of Cyanobacteria and Cyanotoxins from Freshwater to Seawater.Toxins (Basel). 2025 Mar 7;17(3):126. doi: 10.3390/toxins17030126. Toxins (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40137899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liquid chromatography-high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry of anatoxins, including new conjugates and reduction products.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2023 Sep;415(22):5281-5296. doi: 10.1007/s00216-023-04836-y. Epub 2023 Jul 29. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2023. PMID: 37507466 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous Analysis of Cyanotoxins β-N-methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA) and Microcystins-RR, -LR, and -YR Using Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS).Molecules. 2023 Sep 21;28(18):6733. doi: 10.3390/molecules28186733. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37764509 Free PMC article.
-
Immunosensors for Assay of Toxic Biological Warfare Agents.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Mar 20;13(3):402. doi: 10.3390/bios13030402. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36979614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Survey of Microcystin-Producing Cyanobacteria in French Lakes of Various Trophic Status Using Environmental and Cyanobacterial Parameters and an Active Mussel Biomonitoring.Toxins (Basel). 2025 May 15;17(5):245. doi: 10.3390/toxins17050245. Toxins (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40423328 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schopf J.W. The Ecology of Cyanobacteria. Springer; Dordrecht, The Netherlands: 2000. The Fossil Record: Tracing the Roots of the Cyanobacterial Lineage.
-
- Chorus I., Welker M. Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water. A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management. 2nd ed. CRC Press; London, UK: 2021. Cyanobacterial toxins; p. 150.
-
- Mohamed Z., Ahmed Z., Bakr A., Hashem M., Alamri S. Detection of free and bound microcystins in tilapia fish from Egyptian fishpond farms and its related public health risk assessment. J. Consum. Prot. Food Saf. 2019;15:37–47. doi: 10.1007/s00003-019-01254-0. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

