Autism Spectrum Disorder and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: Shared or Unique Neurocognitive Profiles?
- PMID: 36006496
- PMCID: PMC9763138
- DOI: 10.1007/s10802-022-00958-6
Autism Spectrum Disorder and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: Shared or Unique Neurocognitive Profiles?
Abstract
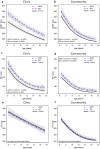
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity (ADHD) and autism spectrum (ASD) disorders are commonly co-occurring conditions characterized by neurocognitive impairments. Few studies have directly compared neurocognitive profiles in ADHD and ASD and fewer still have controlled for comorbidity of ADHD and ASD. All direct comparisons have been in clinic samples, leaving the question of generalizability of results unaddressed. We compared neurocognitive performance in clinically ascertained ASD (n = 261) and ADHD (n = 423) cases and controls (n = 162), 6.0-17.9 years of age. We also compared ASD (n = 190) and ADHD (n = 926) cases ascertained in the community with controls (n = 14,842) of similar age. Using the stop-signal task (SST), we measured response inhibition (stop-signal reaction time-SSRT), sustained attention (defined as reaction time variability-RTV), and reaction time (RT). We controlled for comorbidity using ADHD and ASD trait scores and categorically-defined ADHD. Compared with controls, both clinic ADHD and ASD had significantly longer SSRT and RTV than controls and did not differ from each other. ADHD traits accounted for neurocognitive impairment in ASD, but not vice versa. There were no group differences for RT. Similar patterns of neurocognitive impairment were observed in the community sample. In the largest direct comparison of ADHD and ASD to date, we found impaired response inhibition and sustained attention in both disorders. However, neurocognitive impairment in ASD was almost completely accounted for by comorbid ADHD. Results generalized in the community sample indicating that referral bias alone did not drive results. Response inhibition and sustained attention likely play a role in ADHD and ASD.
Keywords: ADHD; ASD; Inhibitory control; Neuro-cognition; Reaction time variability; Stop-signal task.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
We have no known conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Albajara Sáenz A, Septier M, Van Schuerbeek P, Baijot S, Deconinck N, Defresne P, Delvenne V, Passeri G, Raeymaekers H, Salvesen L, Victoor L, Villemonteix T, Willaye E, Peigneux P, Massat I. ADHD and ASD: distinct brain patterns of inhibition-related activation? Translational Psychiatry. 2020;10(1):24. doi: 10.1038/S41398-020-0707-Z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Albaugh MD, Orr C, Chaarani B, Althoff RR, Allgaier N, D’Alberto N, Hudson K, Mackey S, Spechler PA, Banaschewski T, Brühl R, Bokde ALW, Bromberg U, Büchel C, Cattrell A, Conrod PJ, Desrivières S, Flor H, Frouin V, Potter AS. Inattention and Reaction Time Variability Are Linked to Ventromedial Prefrontal Volume in Adolescents. Biological Psychiatry. 2017;82(9):660–668. doi: 10.1016/J.BIOPSYCH.2017.01.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- APA . Diagnositic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 4. American Psychiatric Publishing; 1994.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
