The Importance of Electrostatics and Polarization for Noncovalent Interactions: Ionic Hydrogen Bonds vs Ionic Halogen Bonds
- PMID: 36006525
- PMCID: PMC9411100
- DOI: 10.1007/s00894-022-05189-6
The Importance of Electrostatics and Polarization for Noncovalent Interactions: Ionic Hydrogen Bonds vs Ionic Halogen Bonds
Abstract
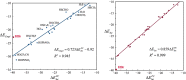
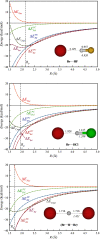
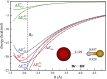
A series of 26 hydrogen-bonded complexes between Br- and halogen, oxygen and sulfur hydrogen-bond (HB) donors is investigated at the M06-2X/6-311 + G(2df,2p) level of theory. Analysis using a model in which Br- is replaced by a point charge shows that the interaction energy ([Formula: see text]) of the complexes is accurately reproduced by the scaled interaction energy with the point charge ([Formula: see text]).This is demonstrated by [Formula: see text] with a correlation coefficient, R2 =0.999. The only outlier is (Br-H-Br)-, which generally is classified as a strong charge-transfer complex with covalent character rather than a HB complex. [Formula: see text] can be divided rigorously into an electrostatic contribution ([Formula: see text]) and a polarization contribution ([Formula: see text]).Within the set of HB complexes investigated, the former varies between -7.2 and -32.7 kcal mol-1, whereas the latter varies between -1.6 and -11.5 kcal mol-1. Compared to our previous study of halogen-bonded (XB) complexes between Br- and C-Br XB donors, the electrostatic contribution is generally stronger and the polarization contribution is generally weaker in the HB complexes. However, for both types of bonding, the variation in interaction strength can be reproduced accurately without invoking a charge-transfer term. For the Br-···HF complex, the importance of charge penetration on the variation of the interaction energy with intermolecular distance is investigated. It is shown that the repulsive character of [Formula: see text] at short distances in this complex to a large extent can be attributed to charge penetration.
Keywords: Charge penetration; Electrostatic potential; Halogen bond; Hydrogen bond; Intermolecular interaction.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Electrostatics and polarization determine the strength of the halogen bond: a red card for charge transfer.J Mol Model. 2019 Apr 24;25(5):125. doi: 10.1007/s00894-019-4014-7. J Mol Model. 2019. PMID: 31020416
-
Examining a Transition from Supramolecular Halogen Bonding to Covalent Bonds: Topological Analysis of Electron Densities and Energies in the Complexes of Bromosubstituted Electrophiles.ACS Omega. 2021 Sep 3;6(36):23588-23597. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c03779. eCollection 2021 Sep 14. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 34549156 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Charge Transfer in Halogen Bonding.J Phys Chem A. 2021 Apr 15;125(14):2944-2953. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpca.1c01412. Epub 2021 Apr 2. J Phys Chem A. 2021. PMID: 33797922
-
Interplay between halogen bonds and hydrogen bonds in OH/SH···HOX···HY (X = Cl, Br; Y = F, Cl, Br) complexes.J Mol Model. 2013 Mar;19(3):1069-77. doi: 10.1007/s00894-012-1657-z. Epub 2012 Nov 1. J Mol Model. 2013. PMID: 23114432
-
Strong N-X⋅⋅⋅O-N Halogen Bonds: A Comprehensive Study on N-Halosaccharin Pyridine N-Oxide Complexes.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019 Dec 16;58(51):18610-18618. doi: 10.1002/anie.201909759. Epub 2019 Nov 7. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019. PMID: 31613414 Review.
Cited by
-
Halogen Bond via an Electrophilic π-Hole on Halogen in Molecules: Does It Exist?Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 23;25(9):4587. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094587. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38731806 Free PMC article.
-
How deeply should we analyze non-covalent interactions?J Mol Model. 2023 Feb 9;29(3):66. doi: 10.1007/s00894-023-05460-4. J Mol Model. 2023. PMID: 36757533 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brinck T, Murray J, Politzer P (1992) Surface electrostatic potentials of halogenated methanes as indicators of directional intermolecular interactions. Int J Quant Chem 57–64.
-
- Koch U, Popelier PLA. Characterization of C-H-O hydrogen bonds on the basis of the charge density. J Phys Chem. 1995;99:9747–9754. doi: 10.1021/j100024a016. - DOI
-
- B Jeziorski, K Szalewicz, Intermolecular Interactions by Perturbation Theory. in Encyclopedia of computational chemistry, 2, edited by P von Rague Schleyer, Allinger, NL, Clark, T., Gasteiger, J., Kollman, PA, Schaefer III, HF, Schreiner, PR (John Wiley and Sons, Chichester, U.K., 1998), 1376.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

