Diagnosis and Treatment of Posteromedial Elbow Impingement in the Throwing Athlete
- PMID: 36006592
- PMCID: PMC9789259
- DOI: 10.1007/s12178-022-09789-w
Diagnosis and Treatment of Posteromedial Elbow Impingement in the Throwing Athlete
Abstract
Purpose of review: Posteromedial elbow impingement is a common pathological entity in the throwing athlete. The posteromedial articulation of the elbow is a significant stabilizer to medial elbow forces and valgus stress noted during repetitive throwing. This current review investigates recent literature regarding the relevant anatomy, diagnosis, and treatment of posteromedial impingement in the thrower.
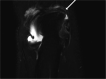
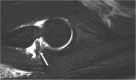
Recent findings: Improvements in advanced imaging have provided accurate and detailed diagnostic capability for the assessment of the throwers' elbow. After failure of conservative measures, arthroscopic treatment of posteromedial elbow impingement with posteromedial osteophyte removal has demonstrated excellent outcomes with a reliable return to play in the competitive thrower. In addition to a thorough history and physical examination, MRI, MR arthrogram, CT, and dynamic ultrasound imaging modalities are useful in the assessment of a presumed diagnosis of posteromedial impingement. Arthroscopic decompression with posteromedial osteophyte removal provides effective clinical results and return to play. The surgeon should be careful to avoid creating medial ulnar collateral instability by means of over-resection of the posteromedial olecranon.
Keywords: Elbow arthroscopy; Elbow impingement; Posteromedial impingement; Thrower’s elbow; Valgus extension overload.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
Robert Bowers declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Gary Lourie declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Timothy Griffith declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

