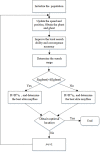
Dynamic elite strategy mayfly algorithm
- PMID: 36006908
- PMCID: PMC9409577
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0273155
Dynamic elite strategy mayfly algorithm
Abstract
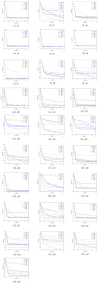
The mayfly algorithm (MA), as a newly proposed intelligent optimization algorithm, is found that easy to fall into the local optimum and slow convergence speed. To address this, an improved mayfly algorithm based on dynamic elite strategy (DESMA) is proposed in this paper. Specifically, it first determines the specific space near the best mayfly in the current population, and dynamically sets the search radius. Then generating a certain number of elite mayflies within this range. Finally, the best one among the newly generated elite mayflies is selected to replace the best mayfly in the current population when the fitness value of elite mayfly is better than that of the best mayfly. Experimental results on 28 standard benchmark test functions from CEC2013 show that our proposed algorithm outperforms its peers in terms of accuracy speed and stability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Global-best brain storm optimization algorithm based on chaotic difference step and opposition-based learning.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 18;14(1):6432. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56919-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38499591 Free PMC article.
-
A hybrid particle swarm optimization algorithm for solving engineering problem.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 10;14(1):8357. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-59034-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38594511 Free PMC article.
-
An Optimal Geometry Configuration Algorithm of Hybrid Semi-Passive Location System Based on Mayfly Optimization Algorithm.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Nov 11;21(22):7484. doi: 10.3390/s21227484. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34833560 Free PMC article.
-
A new Gondwanan mayfly family from the Lower Cretaceous Crato Formation, Brazil (Ephemeroptera: Siphlonuroidea: Astraeopteridae fam. nov.).Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 20;13(1):11735. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-36778-x. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37474555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Why are mayflies (Ephemeroptera) lost following small increases in salinity? Three conceptual osmophysiological hypotheses.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018 Dec 3;374(1764):20180021. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2018.0021. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30509920 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An efficient parallel runoff forecasting model for capturing global and local feature information.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 11;15(1):12423. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-96940-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40216931 Free PMC article.
-
Improved slime mould algorithm based on hybrid strategy optimization of Cauchy mutation and simulated annealing.PLoS One. 2023 Jan 25;18(1):e0280512. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0280512. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36696386 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tutunov R, Bou-Ammar H, Jadbabaie A. Distributed newton method for large-scale consensus optimization. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2019, 64(10), 3983–3994.
-
- Zheng Q, Tian X, Jiang N, Yang M. Layer-wise learning based stochastic gradient descent method for the optimization of deep convolutional neural network. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems, 2019, 37(4), 5641–5654.
-
- Dong HB, Li DJ, Zhang XP. A particle swarm optimization algorithm with dynamically adjusting inertia weight. Computer science, 2018, 45(02):98–102+139.
-
- Irjalili S, Mirjalili SM, Lewis A. Grey wolf optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 69, 2014: 46–61.10.1016/j.advengsoft. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources