Measuring the impact of social-distancing, testing, and undetected asymptomatic cases on the diffusion of COVID-19
- PMID: 36006926
- PMCID: PMC9409553
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0273469
Measuring the impact of social-distancing, testing, and undetected asymptomatic cases on the diffusion of COVID-19
Abstract
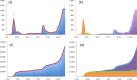
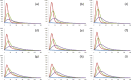
The key to overcoming COVID-19 lies, arguably, in the diffusion process of confirmed cases. In view of this, this study has two main aims: first, to investigate the unique characteristics of COVID-19-for the existence of asymptomatic cases-and second, to determine the best strategy to suppress the diffusion of COVID-19. To this end, this study proposes a new compartmental model-the SICUR model-which can address undetected asymptomatic cases and considers the three main drivers of the diffusion of COVID-19: the degree of social distancing, the speed of testing, and the detection rate of infected cases. Taking each country's situation into account, it is suggested that susceptible cases can be classified into two categories based on their sources of occurrence: internal and external factors. The results show that the ratio of undetected asymptomatic cases to infected cases will, ceteris paribus, be 6.9% for South Korea and 22.4% for the United States. This study also quantitatively shows that to impede the diffusion of COVID-19: firstly, strong social distancing is necessary when the detection rate is high, and secondly, fast testing is effective when the detection rate is low.
Conflict of interest statement
The author has declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Estimation of undetected symptomatic and asymptomatic cases of COVID-19 infection and prediction of its spread in the USA.J Med Virol. 2021 May;93(5):3202-3210. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26897. Epub 2021 Mar 9. J Med Virol. 2021. PMID: 33620096 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of COVID-19 Management Policies Tailored to Airborne SARS-CoV-2 Transmission: Policy Analysis.JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2021 Apr 21;7(4):e20699. doi: 10.2196/20699. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2021. PMID: 33729168 Free PMC article.
-
Transmission dynamics and control of two epidemic waves of SARS-CoV-2 in South Korea.BMC Infect Dis. 2021 May 26;21(1):485. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06204-6. BMC Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34039296 Free PMC article.
-
Estimating The Possible Role Of Testing Capacity And Social Distancing In Predicting The Growth Rate Of Daily Covid-19 Cases.J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2020 Oct-Dec;32(Suppl 1)(4):S686-S690. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2020. PMID: 33754532
-
Universal screening for SARS-CoV-2 infection: a rapid review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Sep 15;9(9):CD013718. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013718. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33502003 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Okabe Y, Shudo A. A Mathematical Model of Epidemics—A Tutorial for Students. Mathematics. 2020;8(7):1174. doi: 10.3390/math8071174 - DOI
-
- Kermack WO, McKendrick AG. A contribution to the mathematical theory of epidemics. Proceedings of the royal society of London Series A, Containing papers of a mathematical and physical character. 1927;115(772):700–721.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

