Aerobic exercise regulates FGF21 and NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis and inhibits atherosclerosis in mice
- PMID: 36006939
- PMCID: PMC9409497
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0273527
Aerobic exercise regulates FGF21 and NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis and inhibits atherosclerosis in mice
Abstract
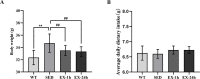
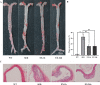
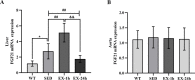
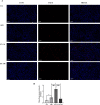
Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21), a known risk factor for atherosclerosis, is readily regulated by exercise, and it can inhibit NOD-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3)-mediated pyroptosis. However, it is not clear whether aerobic exercise inhibits atherosclerosis via these pathways. Eight-week-old apolipoprotein E-deficient (ApoE-/-) mice on a high-fat diet were randomly divided into 1-h post-exercise (EX-1h), 24-h post-exercise (EX-24h), and sedentary (SED) groups. C57BL/6J wild-type mice fed normal chow served as controls (WT group). Mice in the EX-1h and EX-24h groups were subjected to treadmill exercise training for 12 weeks. Aerobic exercise reduced body weight; blood glucose, lipid, and inflammation levels; and aortic plaque area proportion. Aerobic exercise increased the sensitivity of FGF21 by upregulating the expression of the downstream receptor adiponectin (ApN); the serum FGF21 level after exercise increased initially, and then decreased. Aerobic exercise downregulated the expression of NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis-related markers in the aorta, and FGF21 may participate in the above process. Meanwhile, the liver may be the tissue source of serum FGF21 during aerobic exercise. In conclusion, aerobic exercise may inhibit atherogenesis by regulating FGF21 and NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis. Our study provides new information on the atherosclerosis-preventing mechanism of aerobic exercise.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Li W, Jeong JH, Park HG, Lee YR, Li M, Lee SK. Endurance exercise training inhibits neointimal formation via enhancement of FOXOs expression in balloon-induced atherosclerosis rat model. Journal of exercise nutrition & biochemistry. 2014;18(1):105–10. Epub 2015/01/08. doi: 10.5717/jenb.2014.18.1.105 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4241940. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

