Domesticated HERV-W env contributes to the activation of the small conductance Ca2+-activated K+ type 2 channels via decreased 5-HT4 receptor in recent-onset schizophrenia
- PMID: 36007838
- PMCID: PMC10006216
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virs.2022.08.005
Domesticated HERV-W env contributes to the activation of the small conductance Ca2+-activated K+ type 2 channels via decreased 5-HT4 receptor in recent-onset schizophrenia
Abstract
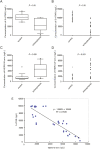
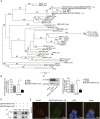
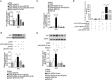
The human endogenous retroviruses type W family envelope (HERV-W env) gene is located on chromosome 7q21-22. Our previous studies show that HERV-W env is elevated in schizophrenia and HERV-W env can increase calcium influx. Additionally, the 5-HTergic system and particularly 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) receptors play a prominent role in the pathogenesis and treatment of schizophrenia. 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 4 (5-HT4R) agonist can block calcium channels. However, the underlying relationship between HERV-W env and 5-HT4R in the etiology of schizophrenia has not been revealed. Here, we used enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to detect the concentration of HERV-W env and 5-HT4R in the plasma of patients with schizophrenia and we found that there were decreased levels of 5-HT4R and a negative correlation between 5-HT4R and HERV-W env in schizophrenia. Overexpression of HERV-W env decreased the transcription and protein levels of 5-HT4R but increased small conductance Ca2+-activated K+ type 2 channels (SK2) expression levels. Further studies revealed that HERV-W env could interact with 5-HT4R. Additionally, luciferase assay showed that an essential region (-364 to -176 from the transcription start site) in the SK2 promoter was required for HERV-W env-induced SK2 expression. Importantly, 5-HT4R participated in the regulation of SK2 expression and promoter activity. Electrophysiological recordings suggested that HERV-W env could increase SK2 channel currents and the increase of SK2 currents was inhibited by 5-HT4R. In conclusion, HERV-W env could activate SK2 channels via decreased 5-HT4R, which might exhibit a novel mechanism for HERV-W env to influence neuronal activity in schizophrenia.
Keywords: 5-Hydroxytryptamine receptor 4 (5-HT4R); Env; Human endogenous retroviruses type W (HERV-W); Schizophrenia; Small conductance Ca(2+)-activated K(+) type 2 channels (SK2).
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
HERV-W env regulates calcium influx via activating TRPC3 channel together with depressing DISC1 in human neuroblastoma cells.J Neurovirol. 2019 Feb;25(1):101-113. doi: 10.1007/s13365-018-0692-7. Epub 2018 Nov 5. J Neurovirol. 2019. PMID: 30397826
-
Human endogenous retrovirus W family envelope gene activates the small conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel in human neuroblastoma cells through CREB.Neuroscience. 2013 Sep 5;247:164-74. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.05.033. Epub 2013 May 28. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 23727510
-
HERV-W Env Induces Neuron Pyroptosis via the NLRP3-CASP1-GSDMD Pathway in Recent-Onset Schizophrenia.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 9;26(2):520. doi: 10.3390/ijms26020520. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39859234 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and regulation of human endogenous retrovirus W elements.APMIS. 2016 Jan-Feb;124(1-2):52-66. doi: 10.1111/apm.12478. APMIS. 2016. PMID: 26818262 Review.
-
Human endogenous retroviruses and multiple sclerosis: innocent bystanders or disease determinants?Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Feb;1812(2):162-76. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2010.07.016. Epub 2010 Aug 6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 20696240 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ERVWE1 Reduces Hippocampal Neuron Density and Impairs Dendritic Spine Morphology through Inhibiting Wnt/JNK Non-Canonical Pathway via miR-141-3p in Schizophrenia.Viruses. 2023 Jan 5;15(1):168. doi: 10.3390/v15010168. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36680208 Free PMC article.
-
Unravelling the Viral Hypothesis of Schizophrenia: A Comprehensive Review of Mechanisms and Evidence.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Aug 1;26(15):7429. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157429. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806558 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HERVs and Cancer-A Comprehensive Review of the Relationship of Human Endogenous Retroviruses and Human Cancers.Biomedicines. 2023 Mar 17;11(3):936. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11030936. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36979914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ancestral retrovirus envelope protein ERVWE1 upregulates circ_0001810, a potential biomarker for schizophrenia, and induces neuronal mitochondrial dysfunction via activating AK2.Cell Biosci. 2024 Nov 14;14(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s13578-024-01318-1. Cell Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39543767 Free PMC article.
-
Human endogenous retrovirus W family envelope protein (ERVWE1) regulates macroautophagy activation and micromitophagy inhibition via NOXA1 in schizophrenia.Virol Sin. 2025 Jun;40(3):401-418. doi: 10.1016/j.virs.2025.05.007. Epub 2025 May 24. Virol Sin. 2025. PMID: 40419114 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abboussi O., Said N., Fifel K., Lakehayli S., Tazi A., El G.S. Behavioral effects of D3 receptor inhibition and 5-HT4 receptor activation on animals undergoing chronic cannabinoid exposure during adolescence. Metab. Brain Dis. 2016;31:321–327. - PubMed
-
- Adelman J.P., Maylie J., Sah P. Small-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels: form and function. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2012;74:245–269. - PubMed
-
- Bickmeyer U., Heine M., Manzke T., Richter D.W. Differential modulation of I(h) by 5-HT receptors in mouse CA1 hippocampal neurons. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2002;16:209–218. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

