Magel2 knockdown in hypothalamic POMC neurons innervating the medial amygdala reduces susceptibility to diet-induced obesity
- PMID: 36007929
- PMCID: PMC9418835
- DOI: 10.26508/lsa.202201502
Magel2 knockdown in hypothalamic POMC neurons innervating the medial amygdala reduces susceptibility to diet-induced obesity
Abstract
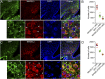
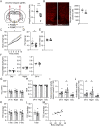
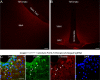
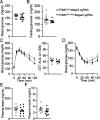
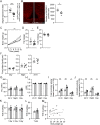
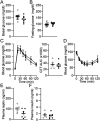
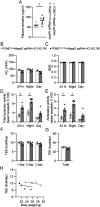
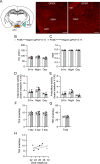
Hyperphagia and obesity profoundly affect the health of children with Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS). The Magel2 gene among the genes in the Prader-Willi syndrome deletion region is expressed in proopiomelanocortin (POMC) neurons in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus (ARC). Knockout of the Magel2 gene disrupts POMC neuronal circuits and functions. Here, we report that loss of the Magel2 gene exclusively in ARCPOMC neurons innervating the medial amygdala (MeA) causes a reduction in body weight in both male and female mice fed with a high-fat diet. This anti-obesity effect is associated with an increased locomotor activity. There are no significant differences in glucose and insulin tolerance in mice without the Magel2 gene in ARCPOMC neurons innervating the MeA. Plasma estrogen levels are higher in female mutant mice than in controls. Blockade of the G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER), but not estrogen receptor-α (ER-α), reduces locomotor activity in female mutant mice. Hence, our study provides evidence that knockdown of the Magel2 gene in ARCPOMC neurons innervating the MeA reduces susceptibility to diet-induced obesity with increased locomotor activity through activation of central GPER.
© 2022 Choi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alfaro DL, Lemoine P, Ehlinger V, Molinas C, Diene G, Valette M, Pinto G, Coupaye M, Poitou-Bernert C, Thuilleaux D, et al. (2019) Causes of death in prader-willi syndrome: Lessons from 11 years’ experience of a national reference center. Orphanet J Rare Dis 14: 238. 10.1186/s13023-019-1214-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Biglari N, Gaziano I, Schumacher J, Radermacher J, Paeger L, Klemm P, Chen W, Corneliussen S, Wunderlich CM, Sue M, et al. (2021) Functionally distinct pomc-expressing neuron subpopulations in hypothalamus revealed by intersectional targeting. Nat Neurosci 24: 913–929. 10.1038/s41593-021-00854-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
