Development and validation of a method to deliver vitamin A to macrophages
- PMID: 36008013
- PMCID: PMC9661891
- DOI: 10.1016/bs.mie.2022.04.008
Development and validation of a method to deliver vitamin A to macrophages
Abstract
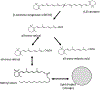
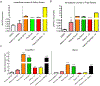
Macrophages are critical players in the development of atherosclerotic lesions, where they promote local and systemic inflammation. Macrophages engulf lipoproteins and cell debris upon entry into the arterial wall, becoming lipid-laden foam cells. While most lipids found in foam cells are triglyceride and cholesterol, these cells accumulate several other lipids with bioactive properties, such as vitamin A and carotenoids. Vitamin A has strong immunomodulatory actions in macrophages and other immune cells. For example, macrophages release vitamin A as retinoic acid to modulate T cell differentiation, but the implication of intracellular vitamin A stores in this process remains elusive due to the lack of an adequate experimental model to load vitamin A into macrophages. The purpose of this study was to develop a reliable method to deliver vitamin A to cultured murine macrophages. Our results show that thioglycolate-elicited peritoneal macrophages fail to take up significant levels of vitamin A when provided as free retinol. Cultured macrophages and macrophages in the peritoneal cavity can take up retinyl esters, either as retinyl ester-loaded serum or retinyl esters infused directly into the peritoneal cavity. HPLC analyses in macrophage lysates revealed that the intraperitoneal injection method results in a fourfold greater vitamin A loading efficiency than retinyl ester-loaded serum added to cultured cells. These two alternative methods provide an efficient and reliable methodology to load macrophages with vitamin A for downstream applications such as studies of gene regulation trafficking of intracellular vitamin A, and vitamin A release from macrophages.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Cardiovascular disease; Chylomicrons; Retinoic acid; Retinoids.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
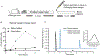


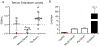
Similar articles
-
Influence of native and modified lipoproteins on migration of mouse peritoneal macrophages and the effect of the antioxidants vitamin E and Probucol.Eur J Cell Biol. 1996 Oct;71(2):199-205. Eur J Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8905298
-
Postchallenge plasma lipoprotein retinoids: chylomicron remnants in endogenous hypertriglyceridemia.Metabolism. 1985 Jun;34(6):551-8. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(85)90193-3. Metabolism. 1985. PMID: 3999977
-
Plasma lipoprotein retinoids after vitamin A feeding in normal man: minimal appearance of retinyl esters among low-density lipoproteins.Metabolism. 1983 May;32(5):514-7. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(83)90016-1. Metabolism. 1983. PMID: 6682471
-
New aspects in vitamin a metabolism: the role of retinyl esters as systemic and local sources for retinol in mucous epithelia.J Nutr. 2004 Dec;134(12 Suppl):3453S-3457S. doi: 10.1093/jn/134.12.3453S. J Nutr. 2004. PMID: 15570053 Review.
-
Disturbed Vitamin A Metabolism in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD).Nutrients. 2017 Dec 29;10(1):29. doi: 10.3390/nu10010029. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 29286303 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immunometabolic effects of β-carotene and vitamin A in atherogenesis.Immunometabolism (Cobham). 2024 Nov 28;6(4):e00051. doi: 10.1097/IN9.0000000000000051. eCollection 2024 Oct. Immunometabolism (Cobham). 2024. PMID: 39624361 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional characterization of interleukin 4 and retinoic acid signaling crosstalk during alternative macrophage activation.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2023 Apr;1868(4):159291. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2023.159291. Epub 2023 Feb 6. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2023. PMID: 36754230 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between blood vitamin A levels and diabetic retinopathy: a population-based study.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 4;14(1):491. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-49937-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38177180 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

