Thymic mimetic cells: tolerogenic masqueraders
- PMID: 36008259
- PMCID: PMC9509455
- DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2022.07.010
Thymic mimetic cells: tolerogenic masqueraders
Abstract
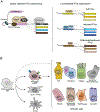
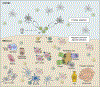
Medullary thymic epithelial cells (mTECs) clonally delete or divert autoreactive T cells by ectopically expressing a diverse array of peripheral-tissue antigens (PTAs) within the thymus. Although thymic stromal cells with histological features of extra-thymic cell types, like myocytes or neurons, have been observed by light microscopy since the mid-1800s, most modern work on PTA expression has focused on the transcription factor Aire. Here, we highlight recent work that has refocused attention on such 'misplaced' thymic cells, referred to collectively as thymic mimetic cells. We review the molecular underpinnings of mimetic cells and their roles in establishing T cell tolerance, and we propose that mimetic cells play important roles in autoimmunity. Finally, we suggest future directions for this emerging area.
Keywords: Aire; T cell tolerance; Thymus; autoimmunity; transcription factor.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests No interests are declared.
Figures
References
-
- Abramson J et al. (2017) Thymic epithelial cells. Annu. Rev Immunol 35, 85–118 - PubMed
-
- Kyewski B et al. (2002) Promiscuous gene expression and central T-cell tolerance: more than meets the eye. Trends Immunol 23, 364–371 - PubMed
-
- Derbinski J et al. (2001) Promiscuous gene expression in medullary thymic epithelial cells mirrors the peripheral self. Nat Immunol 2, 1032–1039 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

