Current status and future perspectives in targeted therapy of NPM1-mutated AML
- PMID: 36008542
- PMCID: PMC9522592
- DOI: 10.1038/s41375-022-01666-2
Current status and future perspectives in targeted therapy of NPM1-mutated AML
Abstract
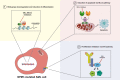
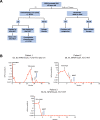
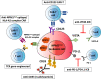
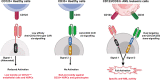
Nucleophosmin 1 (NPM1) is a nucleus-cytoplasmic shuttling protein which is predominantly located in the nucleolus and exerts multiple functions, including regulation of centrosome duplication, ribosome biogenesis and export, histone assembly, maintenance of genomic stability and response to nucleolar stress. NPM1 mutations are the most common genetic alteration in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), detected in about 30-35% of adult AML and more than 50% of AML with normal karyotype. Because of its peculiar molecular and clinico-pathological features, including aberrant cytoplasmic dislocation of the NPM1 mutant and wild-type proteins, lack of involvement in driving clonal hematopoiesis, mutual exclusion with recurrent cytogenetic abnormalities, association with unique gene expression and micro-RNA profiles and high stability at relapse, NPM1-mutated AML is regarded as a distinct genetic entity in the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of hematopoietic malignancies. Starting from the structure and functions of NPM1, we provide an overview of the potential targeted therapies against NPM1-mutated AML and discuss strategies aimed at interfering with the oligomerization (compound NSC348884) and the abnormal traffic of NPM1 (avrainvillamide, XPO1 inhibitors) as well as at inducing selective NPM1-mutant protein degradation (ATRA/ATO, deguelin, (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate, imidazoquinoxaline derivatives) and at targeting the integrity of nucleolar structure (actinomycin D). We also discuss the current therapeutic results obtained in NPM1-mutated AML with the BCL-2 inhibitor venetoclax and the preliminary clinical results using menin inhibitors targeting HOX/MEIS1 expression. Finally, we review various immunotherapeutic approaches in NPM1-mutated AML, including immune check-point inhibitors, CAR and TCR T-cell-based therapies against neoantigens created by the NPM1 mutations.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
MPM declares honoraria from Rasna Therapeutics, Inc for scientific advisor activities and serves as consultant for scientific advisory boards of Abbvie, Amgen, Celgene, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer and Jazz Pharmaceuticals. LB declares consultancy at scientific advisory boards for Abbvie and Amgen. BF licensed a patent on NPM1 mutants (n. 102004901256449) and declares honoraria from Rasna Therapeutics, Inc for scientific advisor activities. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Borer RA, Lehner CF, Eppenberger HM, Nigg EA. Major nucleolar proteins shuttle between nucleus and cytoplasm. Cell. 1989;56:379–90. - PubMed
-
- Grisendi S, Mecucci C, Falini B, Pandolfi PP. Nucleophosmin and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:493–505. - PubMed
-
- Falini B, Mecucci C, Tiacci E, Alcalay M, Rosati R, Pasqualucci L, et al. Cytoplasmic nucleophosmin in acute myelogenous leukemia with a normal karyotype. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:254–66. - PubMed
-
- Falini B, Brunetti L, Sportoletti P, Martelli MP. NPM1-mutated acute myeloid leukemia: from bench to bedside. Blood. 2020;136:1707–21. - PubMed
-
- Alcalay M, Tiacci E, Bergomas R, Bigerna B, Venturini E, Minardi SP, et al. Acute myeloid leukemia bearing cytoplasmic nucleophosmin (NPMc+ AML) shows a distinct gene expression profile characterized by up-regulation of genes involved in stem-cell maintenance. Blood. 2005;106:899–902. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

