Integrated transcriptomic and transgenic analyses reveal potential mechanisms of poplar resistance to Alternaria alternata infection
- PMID: 36008749
- PMCID: PMC9404672
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-022-03793-5
Integrated transcriptomic and transgenic analyses reveal potential mechanisms of poplar resistance to Alternaria alternata infection
Abstract
Background: Populus davidiana × P. bollena is a species of poplar from northeastern China that is characterized by cold resistance and fast growth but now suffers from pathogen infections. Leaf blight caused by Alternaria alternata has become a common poplar disease that causes serious economic impacts, but the molecular mechanisms of resistance to A. alternata in P. davidiana × P. bollena are still unclear.
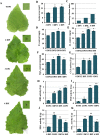
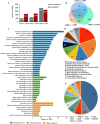
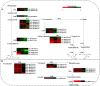
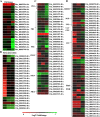
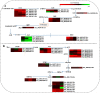
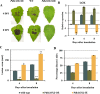
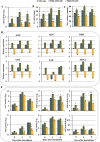
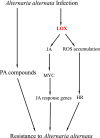
Results: In this study, the transcriptomic response of P. davidiana × P. bollena to A. alternata infection was determined via RNA-Seq. Twelve cDNA libraries were generated from RNA isolated from three biological replicates at four time points (0, 2, 3, and 4 d post inoculation), and a total of 5,930 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were detected (| log2 fold change |≥ 1 and FDR values < 0.05). Functional analysis revealed that the DEGs were mainly enriched for the "plant hormone signal transduction" pathway, followed by the "phenylpropanoid biosynthesis" pathway. In addition, DEGs that encode defense-related proteins and are related to ROS metabolism were also identified. Numerous transcription factors, such as the bHLH, WRKY and MYB families, were also induced by A. alternata infection. Among these DEGs, those related to JA biosynthesis and JA signal transduction were consistently activated. Therefore, the lipoxygenase gene PdbLOX2, which is involved in JA biosynthesis, was selected for functional characterization. Overexpression of PdbLOX2 enhanced the resistance of P. davidiana × P. bollena to A. alternata, whereas silencing this gene enhanced susceptibility to A. alternata infection.
Conclusions: These results provide new insight into the molecular mechanisms of poplar resistance to A. alternata infection and provide candidate genes for breeding resistant cultivars using genetic engineering.
Keywords: Alternaria alternate; Defense response; Lipoxygenase gene; Poplar; RNA-Seq.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Integrative transcriptome and WGCNA analysis reveal key genes mainly in response to Alternaria alternata in Populus simonii × P. nigra.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Feb 17;16:1540718. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1540718. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40034158 Free PMC article.
-
Expression pattern of the poplar GSTU family members in response to Alternaria alternate and PdbGSTU10 confers A. alternate resistance to Populus davidiana × P. bolleana.Plant Sci. 2024 Sep;346:112170. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2024.112170. Epub 2024 Jun 19. Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38906181
-
Expression patterns of the poplar NF-Y gene family in response to Alternaria alternata and hormone treatment and the role of PdbNF-YA11 in disease resistance.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Sep 16;10:956271. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.956271. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36185440 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of two regulatory networks related to salt stress and lignocellulosic synthesis under salt stress based on a Populus davidiana × P. bolleana transcriptome analysis.Plant Mol Biol. 2022 Aug;109(6):689-702. doi: 10.1007/s11103-022-01267-8. Epub 2022 Apr 29. Plant Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35486290
-
Transcriptomics Analysis of Apple Leaves in Response to Alternaria alternata Apple Pathotype Infection.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Jan 20;8:22. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00022. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28163714 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Transcriptome Sequencing and WGCNA Reveal Key Genes in Response to Leaf Blight in Poplar.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 12;24(12):10047. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210047. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373194 Free PMC article.
-
Jasmonic Acid as a Mediator in Plant Response to Necrotrophic Fungi.Cells. 2023 Mar 27;12(7):1027. doi: 10.3390/cells12071027. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37048100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NaLRR-RK4 mediates MAPK signaling to enhance plant defense against Alternaria alternata in Nicotiana attenuata.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):20491. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-04602-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40592980 Free PMC article.
-
Editing Metabolism, Sex, and Microbiome: How Can We Help Poplar Resist Pathogens?Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 21;25(2):1308. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021308. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38279306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrative transcriptome and WGCNA analysis reveal key genes mainly in response to Alternaria alternata in Populus simonii × P. nigra.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Feb 17;16:1540718. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1540718. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40034158 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

