Tumor-Promoting ATAD2 and Its Preclinical Challenges
- PMID: 36008934
- PMCID: PMC9405547
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12081040
Tumor-Promoting ATAD2 and Its Preclinical Challenges
Abstract
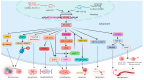
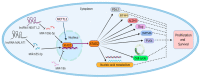
ATAD2 has received extensive attention in recent years as one prospective oncogene with tumor-promoting features in many malignancies. ATAD2 is a highly conserved bromodomain family protein that exerts its biological functions by mainly AAA ATPase and bromodomain. ATAD2 acts as an epigenetic decoder and transcription factor or co-activator, which is engaged in cellular activities, such as transcriptional regulation, DNA replication, and protein modification. ATAD2 has been reported to be highly expressed in a variety of human malignancies, including gastrointestinal malignancies, reproductive malignancies, urological malignancies, lung cancer, and other types of malignancies. ATAD2 is involved in the activation of multiple oncogenic signaling pathways and is closely associated with tumorigenesis, progression, chemoresistance, and poor prognosis, but the oncogenic mechanisms vary in different cancer types. Moreover, the direct targeting of ATAD2's bromodomain may be a very challenging task. In this review, we summarized the role of ATAD2 in various types of malignancies and pointed out the pharmacological direction.
Keywords: ATAD2; bromodomain; malignant tumor; pharmacology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict to interest.
Figures

References
-
- Caron C., Lestrat C., Marsal S., Escoffier E., Curtet S., Virolle V., Barbry P., Debernardi A., Brambilla C., Brambilla E., et al. Functional characterization of ATAD2 as a new cancer/testis factor and a predictor of poor prognosis in breast and lung cancers. Oncogene. 2010;29:5171–5181. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.259. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

