Nanoscale Technologies in the Fight against COVID-19: From Innovative Nanomaterials to Computer-Aided Discovery of Potential Antiviral Plant-Derived Drugs
- PMID: 36008954
- PMCID: PMC9405735
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12081060
Nanoscale Technologies in the Fight against COVID-19: From Innovative Nanomaterials to Computer-Aided Discovery of Potential Antiviral Plant-Derived Drugs
Abstract
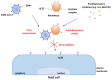
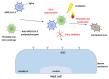
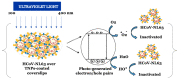
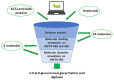
The last few years have increasingly emphasized the need to develop new active antiviral products obtained from artificial synthesis processes using nanomaterials, but also derived from natural matrices. At the same time, advanced computational approaches have found themselves fundamental in the repurposing of active therapeutics or for reducing the very long developing phases of new drugs discovery, which represents a real limitation, especially in the case of pandemics. The first part of the review is focused on the most innovative nanomaterials promising both in the field of therapeutic agents, as well as measures to control virus spread (i.e., innovative antiviral textiles). The second part of the review aims to show how computer-aided technologies can allow us to identify, in a rapid and therefore constantly updated way, plant-derived molecules (i.e., those included in terpenoids) potentially able to efficiently interact with SARS-CoV-2 cell penetration pathways.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; antiviral activity; drug delivery systems; molecular docking; nanodecoys; nanosystems; terpenoids; virus spread control measures.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Emerging nanotechnology role in the development of innovative solutions against COVID-19 pandemic.Nanotechnology. 2021 Sep 8;32(48). doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/ac189e. Nanotechnology. 2021. PMID: 34320471 Review.
-
Emerging strategies on in silico drug development against COVID-19: challenges and opportunities.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2020 Dec 1;155:105522. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105522. Epub 2020 Aug 20. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2020. PMID: 32827661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19: Underpinning Research for Detection, Therapeutics, and Vaccines Development.Pharm Nanotechnol. 2020;8(4):323-353. doi: 10.2174/2211738508999200817163335. Pharm Nanotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32811406 Review.
-
Antiviral properties of copper and its alloys to inactivate covid-19 virus: a review.Biometals. 2021 Dec;34(6):1217-1235. doi: 10.1007/s10534-021-00339-4. Epub 2021 Aug 16. Biometals. 2021. PMID: 34398357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug repurposing for identification of potential spike inhibitors for SARS-CoV-2 using molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations.Methods. 2022 Jul;203:498-510. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2022.02.004. Epub 2022 Feb 12. Methods. 2022. PMID: 35167916 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Institutional Strategies to Maintain and Grow Imaging Research During the COVID-19 Pandemic.Acad Radiol. 2023 Apr;30(4):631-639. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2022.12.045. Epub 2023 Jan 6. Acad Radiol. 2023. PMID: 36764883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fabrication and characteristics of new quaternized chitosan nanocapsules loaded with thymol or thyme essential oil as effective SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors.RSC Adv. 2024 Sep 16;14(40):29330-29343. doi: 10.1039/d4ra03298e. eCollection 2024 Sep 12. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39285882 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. [(accessed on 4 June 2022)]. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

