Thiophosphate Analogs of Coenzyme A and Its Precursors-Synthesis, Stability, and Biomimetic Potential
- PMID: 36008959
- PMCID: PMC9405834
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12081065
Thiophosphate Analogs of Coenzyme A and Its Precursors-Synthesis, Stability, and Biomimetic Potential
Abstract
Coenzyme A (CoA) is ubiquitous and essential for key cellular processes in any living organism. Primary degradation of CoA occurs by enzyme-mediated pyrophosphate hydrolysis intracellularly and extracellularly to form adenosine 3',5'-diphosphate and 4'-phosphopantetheine (PPanSH). The latter can be recycled for intracellular synthesis of CoA. Impairments in the CoA biosynthetic pathway are linked to a severe form of neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation for which no disease-modifying therapy is available. Currently, exogenous administration of PPanSH is examined as a therapeutic intervention. Here, we describe biosynthetic access to thiophosphate analogs of PPanSH, 3'-dephospho-CoA, and CoA. The stabilizing effect of thiophosphate modifications toward degradation by extracellular and peroxisomal enzymes was studied in vitro. Experiments in a CoA-deficient cell model suggest a biomimetic potential of the PPanSH thiophosphate analog PSPanSH (C1). According to our findings, the administration of PSPanSH may provide an alternative approach to support intracellular CoA-dependent pathways.
Keywords: CoA; CoA biosynthesis; CoA deficiency; CoA degradation; HoPan; NBIA; Nudt7; PKAN; PPanSH; phosphorothioate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
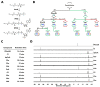
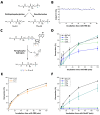
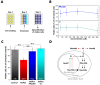
References
-
- Srinivasan B., Baratashvili M., van der Zwaag M., Kanon B., Colombelli C., Lambrechts R.A., Schaap O., Nollen E.A., Podgoršek A., Kosec G., et al. Extracellular 4′-phosphopantetheine is a source for intracellular coenzyme A synthesis. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015;11:784–792. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1906. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

