Anti-Inflammatory microRNAs for Treating Inflammatory Skin Diseases
- PMID: 36008966
- PMCID: PMC9405611
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12081072
Anti-Inflammatory microRNAs for Treating Inflammatory Skin Diseases
Abstract
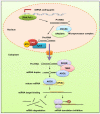
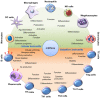
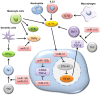
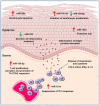
Skin inflammation occurs due to immune dysregulation because of internal disorders, infections, and allergic reactions. The inflammation of the skin is a major sign of chronic autoimmune inflammatory diseases, such as psoriasis, atopic dermatitis (AD), and lupus erythematosus. Although there are many therapies for treating these cutaneous inflammation diseases, their recurrence rates are high due to incomplete resolution. MicroRNA (miRNA) plays a critical role in skin inflammation by regulating the expression of protein-coding genes at the posttranscriptional level during pathogenesis and homeostasis maintenance. Some miRNAs possess anti-inflammatory features, which are beneficial for mitigating the inflammatory response. miRNAs that are reduced in inflammatory skin diseases can be supplied transiently using miRNA mimics and agomir. miRNA-based therapies that can target multiple genes in a given pathway are potential candidates for the treatment of skin inflammation. This review article offers an overview of the function of miRNA in skin inflammation regulation, with a focus on psoriasis, AD, and cutaneous wounds. Some bioactive molecules can target and modulate miRNAs to achieve the objective of inflammation suppression. This review also reports the anti-inflammatory efficacy of these molecules through modulating miRNA expression. The main limitations of miRNA-based therapies are rapid biodegradation and poor skin and cell penetration. Consideration was given to improving these drawbacks using the approaches of cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs), nanocarriers, exosomes, and low-frequency ultrasound. A formulation design for successful miRNA delivery into skin and target cells is also described in this review. The possible use of miRNAs as biomarkers and therapeutic modalities could open a novel opportunity for the diagnosis and treatment of inflammation-associated skin diseases.
Keywords: anti-inflammation; inflammatory disease; keratinocyte; microRNA; skin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNAs in Several Cutaneous Autoimmune Diseases: Psoriasis, Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus and Atopic Dermatitis.Cells. 2020 Dec 10;9(12):2656. doi: 10.3390/cells9122656. Cells. 2020. PMID: 33321931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miRNA expression profiles of the perilesional skin of atopic dermatitis and psoriasis patients are highly similar.Sci Rep. 2022 Dec 31;12(1):22645. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-27235-2. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36587063 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs: Emerging Regulators of Immune-Mediated Diseases.Scand J Immunol. 2012 Feb;75(2):129-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.2011.02650.x. Scand J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 21988491 Review.
-
MicroRNAs: novel regulators in skin inflammation.Clin Exp Dermatol. 2008 May;33(3):312-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.2008.02804.x. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2008. PMID: 18419608 Review.
-
MicroRNAs in atopic dermatitis: A systematic review.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Jun;24(11):5966-5972. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15208. Epub 2020 Apr 30. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32351034 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
MiR-126-5p Down-Regulation Alleviates the Inflammatory Response of Allergic Rhinitis in Children via Inhibiting HIPK2/NF-κB Signaling Pathway.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Mar 17;18:3981-3992. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S507828. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40125082 Free PMC article.
-
Resolution of Chronic Inflammation, Restoration of Epigenetic Disturbances and Correction of Dysbiosis as an Adjunctive Approach to the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis.Cells. 2024 Nov 18;13(22):1899. doi: 10.3390/cells13221899. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39594647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Skin Disorders and Osteoporosis: Unraveling the Interplay Between Vitamin D, Microbiota, and Epigenetics Within the Skin-Bone Axis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 28;26(1):179. doi: 10.3390/ijms26010179. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39796035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-22-mediated microRNA-124-3p/GRB2 axis regulates hyperproliferation and inflammatory response of keratinocytes in psoriasis.Arch Dermatol Res. 2025 Jan 10;317(1):227. doi: 10.1007/s00403-024-03668-9. Arch Dermatol Res. 2025. PMID: 39792268
-
Promising strategies in natural products treatments of psoriasis-update.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Sep 4;11:1386783. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1386783. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39296901 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

