Cisplatin-Induced Kidney Toxicity: Potential Roles of Major NAD+-Dependent Enzymes and Plant-Derived Natural Products
- PMID: 36008971
- PMCID: PMC9405866
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12081078
Cisplatin-Induced Kidney Toxicity: Potential Roles of Major NAD+-Dependent Enzymes and Plant-Derived Natural Products
Abstract
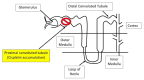
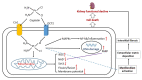
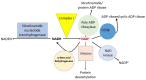
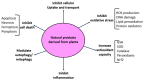
Cisplatin is an FDA approved anti-cancer drug that is widely used for the treatment of a variety of solid tumors. However, the severe adverse effects of cisplatin, particularly kidney toxicity, restrict its clinical and medication applications. The major mechanisms of cisplatin-induced renal toxicity involve oxidative stress, inflammation, and renal fibrosis, which are covered in this short review. In particular, we review the underlying mechanisms of cisplatin kidney injury in the context of NAD+-dependent redox enzymes including mitochondrial complex I, NAD kinase, CD38, sirtuins, poly-ADP ribosylase polymerase, and nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase (NNT) and their potential contributing roles in the amelioration of cisplatin-induced kidney injury conferred by natural products derived from plants. We also cover general procedures used to create animal models of cisplatin-induced kidney injury involving mice and rats. We highlight the fact that more studies will be needed to dissect the role of each NAD+-dependent redox enzyme and its involvement in modulating cisplatin-induced kidney injury, in conjunction with intensive research in NAD+ redox biology and the protective effects of natural products against cisplatin-induced kidney injury.
Keywords: cisplatin; kidney toxicity; mitochondria; natural products; oxidative stress; redox imbalance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ashrafi F., Mortazavi M., Nematbakhsh M. The prevention of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity: A general consensus statement of a group of oncologist-hematologists, adult and pediatric nephrologists, radiation oncologists, clinical pathologists, clinical pharmacologists, and renal physiologists on cisplatin therapy in cancer patients. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2022;13:21. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cohen S.M., Lippard S.J. Cisplatin: From DNA damage to cancer chemotherapy. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 2001;67:93–130. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

