The Effect of β-Carotene, Tocopherols and Ascorbic Acid as Anti-Oxidant Molecules on Human and Animal In Vitro/In Vivo Studies: A Review of Research Design and Analytical Techniques Used
- PMID: 36008981
- PMCID: PMC9406122
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12081087
The Effect of β-Carotene, Tocopherols and Ascorbic Acid as Anti-Oxidant Molecules on Human and Animal In Vitro/In Vivo Studies: A Review of Research Design and Analytical Techniques Used
Abstract
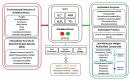
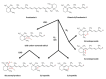
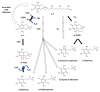
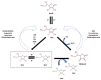
Prolonged elevated oxidative stress (OS) possesses negative effect on cell structure and functioning, and is associated with the development of numerous disorders. Naturally occurred anti-oxidant compounds reduce the oxidative stress in living organisms. In this review, antioxidant properties of β-carotene, tocopherols and ascorbic acid are presented based on in vitro, in vivo and populational studies. Firstly, environmental factors contributing to the OS occurrence and intracellular sources of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) generation, as well as ROS-mediated cellular structure degradation, are introduced. Secondly, enzymatic and non-enzymatic mechanism of anti-oxidant defence against OS development, is presented. Furthermore, ROS-preventing mechanisms and effectiveness of β-carotene, tocopherols and ascorbic acid as anti-oxidants are summarized, based on studies where different ROS-generating (oxidizing) agents are used. Oxidative stress biomarkers, as indicators on OS level and prevention by anti-oxidant supplementation, are presented with a focus on the methods (spectrophotometric, fluorometric, chromatographic, immuno-enzymatic) of their detection. Finally, the application of Raman spectroscopy and imaging as a tool for monitoring the effect of anti-oxidant (β-carotene, ascorbic acid) on cell structure and metabolism, is proposed. Literature data gathered suggest that β-carotene, tocopherols and ascorbic acid possess potential to mitigate oxidative stress in various biological systems. Moreover, Raman spectroscopy and imaging can be a valuable technique to study the effect of oxidative stress and anti-oxidant molecules in cell studies.
Keywords: antioxidants; biomarkers; oxidative stress; raman spectroscopy and imaging; reactive oxygen species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sharma P., Jha A.B., Dubey R.S., Pessarakli M. Reactive Oxygen Species, Oxidative Damage, and Antioxidative Defense Mechanism in Plants under Stressful Conditions. J. Bot. 2012;2012:217037. doi: 10.1155/2012/217037. - DOI
-
- Juan C.A., Pérez de la Lastra J.M., Plou F.J., Pérez-Lebeña E. The Chemistry of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Revisited: Outlining Their Role in Biological Macromolecules (DNA, Lipids and Proteins) and Induced Pathologies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021;22:4642. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094642. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pędziwiatr P., Mikołajczyk F., Zawadzki D., Mikołajczyk K., Bedka A. Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide-Kinetics and Review of Chosen Catalysts. Acta Innov. 2018;26:45–52. doi: 10.32933/ActaInnovations.26.5. - DOI
-
- Haider M.S., Jaskani M.J., Fang J. Biocontrol Agents and Secondary Metabolites. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2021. Overproduction of ROS: Underlying Molecular Mechanism of Scavenging and Redox Signaling; pp. 347–382.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

