(3α,5α)3-Hydroxypregnan-20-one (3α,5α-THP) Regulation of the HPA Axis in the Context of Different Stressors and Sex
- PMID: 36009028
- PMCID: PMC9406198
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12081134
(3α,5α)3-Hydroxypregnan-20-one (3α,5α-THP) Regulation of the HPA Axis in the Context of Different Stressors and Sex
Abstract
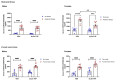
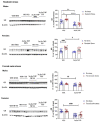
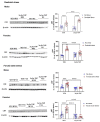
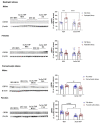
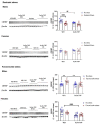
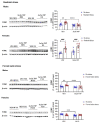
Corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) regulates the stress response in the hypothalamus and modulates neurotransmission across the brain through CRF receptors. Acute stress increases hypothalamic CRF and the GABAergic neurosteroid (3α,5α)3-hydroxypregnan-20-one (3α,5α-THP). We previously showed that 3α,5α-THP regulation of CRF is sex and brain region dependent. In this study, we investigated 3α,5α-THP regulation of stress-induced hypothalamic CRF, CRF receptor type 1 (CRFR1), CRF binding protein (CRFBP), pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC), and glucocorticoid receptor (GR) by western blot and circulating corticosterone (CORT) by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in male and female Sprague Dawley rats. Tissue was collected after rats were injected with 3α,5α-THP (15 mg/kg, IP) or vehicle 15 min prior to 30 min of restraint stress (RS), or 10 min of forced swim stress (FSS) and 20 min recovery. The initial exposure to a stress stimulus increased circulating CORT levels in both males and females, but 3α,5α-THP attenuated the CORT response only in females after RS. 3α,5α-THP reduced GR levels in male and females, but differently between stressors. 3α,5α-THP decreased the CRF stress response after FSS in males and females, but after RS, only in female rats. 3α,5α-THP reduced the CRFR1, CRFBP, and POMC increases after RS and FSS in males, but in females only after FSS. Our results showed different stress responses following different types of stressors: 3α,5α-THP regulated the HPA axis at different levels, depending on sex.
Keywords: 3α,5α-THP; CRF; CRFR1; HPA axis; allopregnanolone; corticosterone; forced swim stress; hypothalamus; neuro-steroids; restraint stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Owens M.J., Nemeroff C.B. Physiology and pharmacology of corticotropin-releasing factor. Pharmacol. Rev. 1991;43:425–473. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

