ADAR2 Protein Is Associated with Overall Survival in GBM Patients and Its Decrease Triggers the Anchorage-Independent Cell Growth Signature
- PMID: 36009036
- PMCID: PMC9405742
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12081142
ADAR2 Protein Is Associated with Overall Survival in GBM Patients and Its Decrease Triggers the Anchorage-Independent Cell Growth Signature
Abstract
Background: Epitranscriptomic mechanisms, such as A-to-I RNA editing mediated by ADAR deaminases, contribute to cancer heterogeneity and patients' stratification. ADAR enzymes can change the sequence, structure, and expression of several RNAs, affecting cancer cell behavior. In glioblastoma, an overall decrease in ADAR2 RNA level/activity has been reported. However, no data on ADAR2 protein levels in GBM patient tissues are available; and most data are based on ADARs overexpression experiments.
Methods: We performed IHC analysis on GBM tissues and correlated ADAR2 levels and patients' overall survival. We silenced ADAR2 in GBM cells, studied cell behavior, and performed a gene expression/editing analysis.
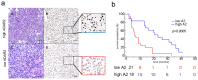
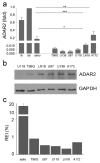
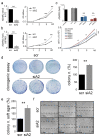
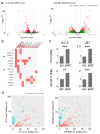
Results: GBM tissues do not all show a low/no ADAR2 level, as expected by previous studies. Although, different amounts of ADAR2 protein were observed in different patients, with a low level correlating with a poor patient outcome. Indeed, reducing the endogenous ADAR2 protein in GBM cells promotes cell proliferation and migration and changes the cell's program to an anchorage-independent growth mode. In addition, deep-seq data and bioinformatics analysis indicated multiple RNAs are differently expressed/edited upon siADAR2.
Conclusion: ADAR2 protein is an important deaminase in GBM and its amount correlates with patient prognosis.
Keywords: ADAM12; ADAR2; PTPX3; RNA editing; anchorage-independent growth; cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of SNORD113-3/ADAR2 on glycolipid metabolism in glioblastoma via A-to-I editing of PHKA2.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025 Jan 10;30(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s11658-024-00680-9. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025. PMID: 39794701 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of microRNA editing, expression and processing by ADAR2 deaminase in glioblastoma.Genome Biol. 2015 Jan 13;16(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0575-z. Genome Biol. 2015. PMID: 25582055 Free PMC article.
-
ADAR2 Regulates Malignant Behaviour of Mesothelioma Cells Independent of RNA-editing Activity.Anticancer Res. 2020 Mar;40(3):1307-1314. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.14072. Anticancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32132027
-
Mechanisms and implications of ADAR-mediated RNA editing in cancer.Cancer Lett. 2017 Dec 28;411:27-34. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.09.036. Epub 2017 Sep 30. Cancer Lett. 2017. PMID: 28974449 Review.
-
ADARs and editing: The role of A-to-I RNA modification in cancer progression.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2018 Jul;79:123-130. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.11.018. Epub 2017 Nov 16. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 29146145 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in A-to-I RNA editing in cancer.Mol Cancer. 2024 Dec 27;23(1):280. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02194-6. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39731127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antitumor Potential of Antiepileptic Drugs in Human Glioblastoma: Pharmacological Targets and Clinical Benefits.Biomedicines. 2023 Feb 16;11(2):582. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11020582. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36831117 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical applications of oligonucleotides for cancer therapy.Mol Ther. 2025 Jun 4;33(6):2705-2718. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2025.02.045. Epub 2025 Mar 5. Mol Ther. 2025. PMID: 40045578 Review.
References
-
- Silvestris D.A., Picardi E., Cesarini V., Fosso B., Mangraviti N., Massimi L., Martini M., Pesole G., Locatelli F., Gallo A. Dynamic inosinome profiles reveal novel patient stratification and gender-specific differences in glioblastoma. Genome Biol. 2019;20:33. doi: 10.1186/s13059-019-1647-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

