Isolation, Purification, and Characterisation of a Phage Tail-Like Bacteriocin from the Insect Pathogenic Bacterium Brevibacillus laterosporus
- PMID: 36009048
- PMCID: PMC9406221
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12081154
Isolation, Purification, and Characterisation of a Phage Tail-Like Bacteriocin from the Insect Pathogenic Bacterium Brevibacillus laterosporus
Abstract
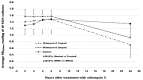
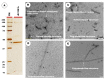
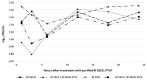
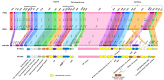
The Gram-positive and spore-forming bacterium Brevibacillus laterosporus (Bl) belongs to the Brevibacillus brevis phylogenetic cluster. Isolates of the species have demonstrated pesticidal potency against a wide range of invertebrate pests and plant diseases. Two New Zealand isolates, Bl 1821L and Bl 1951, are under development as biopesticides for control of diamondback moth and other pests. However, due to the often-restricted growth of these endemic isolates, production can be an issue. Based on the previous work, it was hypothesised that the putative phages might be involved. During investigations of the cause of the disrupted growth, electron micrographs of crude lysate of Bl 1821L showed the presence of phages’ tail-like structures. A soft agar overlay method with PEG 8000 precipitation was used to differentiate between the antagonistic activity of the putative phage and phage tail-like structures (bacteriocins). Assay tests authenticated the absence of putative phage activity. Using the same method, broad-spectrum antibacterial activity of Bl 1821L lysate against several Gram-positive bacteria was found. SDS-PAGE of sucrose density gradient purified and 10 kD MWCO concentrated lysate showed a prominent protein band of ~48 kD, and transmission electron microscopy revealed the presence of polysheath-like structures. N-terminal sequencing of the ~48 kD protein mapped to a gene with weak predicted amino acid homology to a Bacillus PBSX phage-like element xkdK, the translated product of which shared >90% amino acid similarity to the phage tail-sheath protein of another Bl published genome, LMG15441. Bioinformatic analysis also identified an xkdK homolog in the Bl 1951 genome. However, genome comparison of the region around the xkdK gene between Bl 1821L and Bl 1951 found differences including two glycine rich protein encoding genes which contain imperfect repeats (1700 bp) in Bl 1951, while a putative phage region resides in the analogous Bl 1821L region. Although comparative analysis of the genomic organisation of Bl 1821L and Bl 1951 PBSX-like region with the defective phages PBSX, PBSZ, and PBP 180 of Bacillus subtilis isolates 168 and W23, and Bacillus phage PBP180 revealed low amino acids similarity, the genes encode similar functional proteins in similar arrangements, including phage tail-sheath (XkdK), tail (XkdO), holin (XhlB), and N-acetylmuramoyl-l-alanine (XlyA). AMPA analysis identified a bactericidal stretch of 13 amino acids in the ~48 kD sequenced protein of Bl 1821L. Antagonistic activity of the purified ~48 kD phage tail-like protein in the assays differed remarkably from the crude lysate by causing a decrease of 34.2% in the number of viable cells of Bl 1951, 18 h after treatment as compared to the control. Overall, the identified inducible phage tail-like particle is likely to have implications for the in vitro growth of the insect pathogenic isolate Bl 1821L.
Keywords: PBSX; antibacterial protein; contractile phage tail-sheath; defective phage; insect pathogenic bacterium.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Linocin M18 protein from the insect pathogenic bacterium Brevibacillus laterosporus isolates.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Jul;107(13):4337-4353. doi: 10.1007/s00253-023-12563-8. Epub 2023 May 19. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37204448 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical characterisation and production kinetics of high molecular-weight (HMW) putative antibacterial proteins of insect pathogenic Brevibacillus laterosporus isolates.BMC Microbiol. 2024 Jul 13;24(1):259. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03340-2. BMC Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38997685 Free PMC article.
-
Biological and genomic analysis of a PBSX-like defective phage induced from Bacillus pumilus AB94180.Arch Virol. 2014 Apr;159(4):739-52. doi: 10.1007/s00705-013-1898-x. Epub 2013 Oct 25. Arch Virol. 2014. PMID: 24154951
-
[Bacteriophages and bacteriocins of the genus Listeria].Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Feb;261(1):12-28. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986. PMID: 3085381 Review. French.
-
Engineering of receptor-binding proteins in bacteriophages and phage tail-like bacteriocins.Biochem Soc Trans. 2019 Feb 28;47(1):449-460. doi: 10.1042/BST20180172. Epub 2019 Feb 19. Biochem Soc Trans. 2019. PMID: 30783013 Review.
Cited by
-
A VersaTile Approach to Reprogram the Specificity of the R2-Type Tailocin Towards Different Serotypes of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae.Antibiotics (Basel). 2025 Jan 18;14(1):104. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics14010104. Antibiotics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39858389 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of Brevibacillus brevis strain TR-4 against leaf disease of Photinia×fraseri Dress.PeerJ. 2024 Jun 25;12:e17568. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17568. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38948232 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary and ecological role of extracellular contractile injection systems: from threat to weapon.Front Microbiol. 2023 Oct 11;14:1264877. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1264877. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37886057 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stress-driven temporal production of phage tail-like particles (tailocins) in Dickeya dadantii strain 3937.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 26;15(1):27234. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-13158-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40715312 Free PMC article.
-
Linocin M18 protein from the insect pathogenic bacterium Brevibacillus laterosporus isolates.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Jul;107(13):4337-4353. doi: 10.1007/s00253-023-12563-8. Epub 2023 May 19. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37204448 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bowen D., Yin Y., Flasinski S., Chay C., Bean G., Milligan J., Moar W., Pan A., Werner B., Buckman K. Cry75Aa (Mpp75Aa) insecticidal proteins for controlling the Western corn rootworm, Diabrotica virgifera virgifera LeConte (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae), isolated from the insect-pathogenic bacterium Brevibacillus laterosporus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021;87:e02507–e02520. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02507-20. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Salama H., Foda M., El-Bendary M., Abdel-Razek A. Infection of red palm weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus, by spore-forming bacilli indigenous to its natural habitat in Egypt. J. Pest Sci. 2004;77:27–31. doi: 10.1007/s10340-003-0023-4. - DOI
-
- Carramaschi I.N., Pereira L.D.A., Queiroz M.M.D.C., Zahner V. Preliminary screening of the larvicidal effect of Brevibacillus laterosporus strains against the blowfly Chrysomya megacephala (Fabricius, 1794) (Diptera: Calliphoridae) Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2015;48:427–431. doi: 10.1590/0037-8682-0092-2015. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

