Periostin Augments Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Calcification via β-Catenin Signaling
- PMID: 36009051
- PMCID: PMC9405747
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12081157
Periostin Augments Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Calcification via β-Catenin Signaling
Abstract
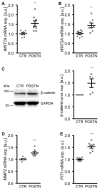
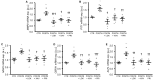
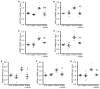
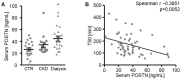
Medial vascular calcification is common in chronic kidney disease (CKD) and is closely linked to hyperphosphatemia. Vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) can take up pro-calcific properties and actively augment vascular calcification. Various pro-inflammatory mediators are able to promote VSMC calcification. In this study, we investigated the effects and mechanisms of periostin, a matricellular signaling protein, in calcifying human VSMCs and human serum samples. As a result, periostin induced the mRNA expression of pro-calcific markers in VSMCs. Furthermore, periostin augmented the effects of β-glycerophosphate on the expression of pro-calcific markers and aggravated the calcification of VSMCs. A periostin treatment was associated with an increased β-catenin abundance as well as the expression of target genes. The pro-calcific effects of periostin were ameliorated by WNT/β-catenin pathway inhibitors. Moreover, a co-treatment with an integrin αvβ3-blocking antibody blunted the pro-calcific effects of periostin. The silencing of periostin reduced the effects of β-glycerophosphate on the expression of pro-calcific markers and the calcification of VSMCs. Elevated serum periostin levels were observed in hemodialysis patients compared with healthy controls. These observations identified periostin as an augmentative factor in VSMC calcification. The pro-calcific effects of periostin involve integrin αvβ3 and the activation of the WNT/β-catenin pathway. Thus, the inhibition of periostin may be beneficial to reduce the burden of vascular calcification in CKD patients.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; periostin; phosphate; vascular calcification; vascular smooth muscle cells; β-catenin.
Conflict of interest statement
A.P. is an employee and stockholder of Calciscon AG, which commercializes the T50 test.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Augmentative effects of leukemia inhibitory factor reveal a critical role for TYK2 signaling in vascular calcification.Kidney Int. 2024 Oct;106(4):611-624. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2024.07.011. Epub 2024 Jul 30. Kidney Int. 2024. PMID: 39084258
-
O-GlcNAc transferase promotes vascular smooth muscle calcification through modulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling.FASEB J. 2024 Dec 13;38(24):e70271. doi: 10.1096/fj.202401649RR. FASEB J. 2024. PMID: 39704274
-
Sclerostin/Receptor Related Protein 4 and Ginkgo Biloba Extract Alleviates β-Glycerophosphate-Induced Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Calcification By Inhibiting Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway.Blood Purif. 2019;47 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):17-23. doi: 10.1159/000496219. Epub 2019 Jan 30. Blood Purif. 2019. PMID: 30699436 Free PMC article.
-
The role of calprotectin in vascular calcification.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2025 Jul 1;34(4):276-283. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000001075. Epub 2025 Mar 29. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2025. PMID: 40152927 Review.
-
Research progress of periostin and osteoporosis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Feb 29;15:1356297. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1356297. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38487345 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Multiple Roles of Periostin in Non-Neoplastic Disease.Cells. 2022 Dec 22;12(1):50. doi: 10.3390/cells12010050. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36611844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Biomarkers of Bone Metabolism.Nutrients. 2024 Feb 22;16(5):605. doi: 10.3390/nu16050605. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38474734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioinspired Collagen/κ-Carrageenan 3D Matrix for In Vitro Modeling of Vascular Calcification.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2025 Aug 11;11(8):5012-5026. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.5c00754. Epub 2025 Jul 19. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2025. PMID: 40682530 Free PMC article.
-
Periostin in Osteoporosis and Cardiovascular Disease.J Endocr Soc. 2023 Jun 16;7(7):bvad081. doi: 10.1210/jendso/bvad081. eCollection 2023 Jun 5. J Endocr Soc. 2023. PMID: 37362382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular matrix in vascular homeostasis and disease.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2025 May;22(5):333-353. doi: 10.1038/s41569-024-01103-0. Epub 2025 Jan 2. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 39743560 Review.
References
-
- Alesutan I., Luong T.T.D., Schelski N., Masyout J., Hille S., Schneider M.P., Graham D., Zickler D., Verheyen N., Estepa M., et al. Circulating uromodulin inhibits vascular calcification by interfering with pro-inflammatory cytokine signalling. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021;117:930–941. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvaa081. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

