The Resistome of ESKAPEE Pathogens in Untreated and Treated Wastewater: A Polish Case Study
- PMID: 36009054
- PMCID: PMC9405806
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12081160
The Resistome of ESKAPEE Pathogens in Untreated and Treated Wastewater: A Polish Case Study
Abstract
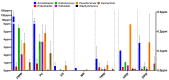
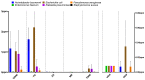
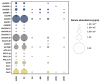
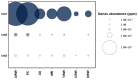
The aim of this study was to quantify ESKAPEE bacteria, genes encoding resistance to antibiotics targeting this group of pathogens, as well as integrase genes in municipal wastewater and river water. Environmental DNA was extracted from the collected samples and used in deep sequencing with the Illumina TruSeq kit. The abundance of bacterial genera and species belonging to the ESKAPEE group, 400 ARGs associated with this microbial group, and three classes of integrase genes were determined. A taxonomic analysis revealed that Acinetobacter was the dominant bacterial genus, whereas Acinetobacter baumannii and Escherichia coli were the dominant bacterial species. The analyzed samples were characterized by the highest concentrations of the following ARGs: blaGES, blaOXA-58, blaTEM, qnrB, and qnrS. Acinetobacter baumannii, E. coli, and genes encoding resistance to β-lactams (blaVEB-1, blaIMP-1, blaGES, blaOXA-58, blaCTX-M, and blaTEM) and fluoroquinolones (qnrS) were detected in samples of river water collected downstream from the wastewater discharge point. The correlation analysis revealed a strong relationship between A. baumannii (bacterial species regarded as an emerging human pathogen) and genes encoding resistance to all tested groups of antimicrobials. The transmission of the studied bacteria (in particular A. baumannii) and ARGs to the aquatic environment poses a public health risk.
Keywords: ESKAPEE; antibiotic resistance; antibiotic resistance genes; river water; wastewater.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Timothy J.F. Antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Curr. Status Future Prospect. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017;41:430–449. - PubMed
-
- Heymann D.L. The World Health Report 2007: A Safer Future: Global Public Health Security in the 21st Century. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2007.
-
- Marano R.B.M., Fernandes T., Manaia C.M., Nunes O., Morrison D., Berendonk T.U., Kreuzinger N., Tenson T., Corno G., Fatta-Kassinos D., et al. A global multinational survey of cefotaxime-resistant coliforms in urban wastewater treatment plants. Environ. Int. 2020;144:106035. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.106035. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

