Resting-State Functional Connectivity Analyses: Brain Functional Reorganization in a Rat Model of Postherpetic Neuralgia
- PMID: 36009092
- PMCID: PMC9405817
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci12081029
Resting-State Functional Connectivity Analyses: Brain Functional Reorganization in a Rat Model of Postherpetic Neuralgia
Abstract
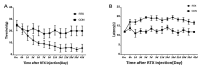
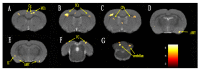
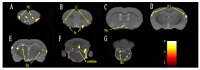
Postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) is a chronic neuropathic pain syndrome, similar to other chronic pains, the mechanisms of which are not fully understood. To further understand the neural mechanism of this chronic pain and its transition, we performed functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) scans on PHN rat models. Twelve PHN rat models were established by intraperitoneal injection of resiniferatoxin, with an additional 12 rats serving as controls. Nociceptive behavioral tests were performed on these rats and fMRI scans were performed on days 7 and 14 after modeling. Functional connection (FC) analysis was used to investigate the brain FC alterations associated with chronic pain in PHN rats, with the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) as a seed. Nociceptive behavioral tests showed that PHN rats presented symptoms similar to those of PHN patients. FC analysis showed that compared to the control group, the PHN group showed different FC patterns on days 7 and 14. As can be seen, the brain FC alterations in the rat model of PHN changed dynamically, shifting from brain regions processing sensory information to regions processing emotions and motives.
Keywords: chronic pain; magnetic resonance imaging; neuralgia; postherpetic; rats.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Matthews S., De Maria A., Passamonti M., Ristori G., Loiacono I., Puggina A., Curran D. Open Forum Infectious Diseases. Volume 6. Oxford University Press; Oxford, UK: 2019. The Economic Burden and Impact on Quality of Life of Herpes Zoster and Postherpetic Neuralgia in Individuals Aged 50 Years or Older in Italy. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- GSWS2020009/Suzhou Gusu Medical Youth Talent
- GSWS2020019/Suzhou Gusu Medical Youth Talent
- 2020WSB06/the Translational Research Grant of NCRCH
- 81971573/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- LCZX201801/the Clinical Key Diseases Diagnosis and Therapy Special Project of Health and Family Planning Commission of Suzhou
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

