Beneficial Influence of Exendin-4 on Specific Organs and Mechanisms Favourable for the Elderly with Concomitant Obstructive Lung Diseases
- PMID: 36009152
- PMCID: PMC9405576
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci12081090
Beneficial Influence of Exendin-4 on Specific Organs and Mechanisms Favourable for the Elderly with Concomitant Obstructive Lung Diseases
Abstract
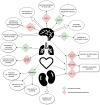
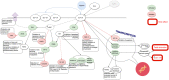
Exendin-4 (Ex-4), better known in its synthetic form and used clinically as exenatide, currently applied in the treatment of diabetes, induces a beneficial impact on nerve cells, and shows promising effects in obstructive lung diseases. At an advanced age, the development of the neurodegenerative process of brain tissue is masked by numerous concomitant diseases. The initial latent phase of neurodegenerative disease results in occurrence of manifestations at an advanced stage. To protect the brain and to simultaneously ensure proper treatment of common coexisting conditions in late life, such as diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or asthma, a pleiotropic medication should be chosen. Molecular mechanisms of Ex-4 exert neuroprotective effects or lead to secondary neurogenesis. Additionally, Ex-4 plays an important role in anti-inflammatory actions which are necessary both in the case of asthma and Parkinson's disease. Specific receptors in the lungs also reduce the secretion of surfactants, which decreases the risk of exacerbation in chronic obstructive lung disease. In a great number of patients suffering from diabetes, asthma, or chronic lung disease, there is a great potential for both treatment of the main condition and protection against brain neurodegeneration.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s; COPD; Ex-4; anti-inflammation; asthma; elderly; hypoxia; neurodegeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Athauda D., Maclagan K., Skene S.S., Bajwa-Joseph M., Letchford D., Chowdhury K., Hibbert S., Budnik N., Zampedri L., Dickson J., et al. Exenatide once weekly versus placebo in Parkinson’s disease: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2017;390:1664–1675. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31585-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li Y., Chigurupati S., Holloway H.W., Mughal M., Tweedie D., Bruestle D.A., Mattson M.P., Wang Y., Harvey B.K., Ray B., et al. Exendin-4 Ameliorates Motor Neuron Degeneration in Cellular and Animal Models of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e32008. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032008. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources