Physiological Performance, Antioxidant and Immune Status, Columnaris Resistance, and Growth of Nile Tilapia That Received Alchemilla vulgaris-Supplemented Diets
- PMID: 36009213
- PMCID: PMC9404728
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11081494
Physiological Performance, Antioxidant and Immune Status, Columnaris Resistance, and Growth of Nile Tilapia That Received Alchemilla vulgaris-Supplemented Diets
Abstract
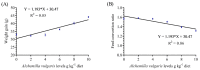
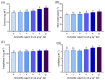
The current perspective is a pioneering trial to assess the efficacy of the dietary supplementation of Alchemilla vulgaris powder (AVP) in the diet of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) on growth performance, blood picture, hepatic and renal biomarkers, immune status, and serum and tissue antioxidant capacity and to investigate the resistance against Flavobacterium columnare challenge. Fish (n = 360) were distributed into six groups (three replicates each) and received increasing AVP supplementation levels (0, 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10 g kg-1) for 60 days. Furthermore, fish were exposed to the bacterial challenge of a virulent F. columnare strain and maintained under observation for 12 days. During the observation period, clinical signs and the cumulative mortality percentage were recorded. The results demonstrated that the growth performance, feed conversion ratio, and hematological profile were noticeably enhanced in the AVP-supplemented groups compared to the control. The most promising results of weight gain and feed conversion ratio were recorded in the groups with 6, 8, and 10 g AVP kg-1 diets in a linear regression trend. The levels of hepatorenal function indicators were maintained in a healthy range in the different dietary AVP-supplemented groups. In a dose-dependent manner, fish fed AVP dietary supplements displayed significant augmented serum levels of innate immune indicators (lysozyme, nitric oxide, and complement 3) and antioxidant biomarkers (Catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), total antioxidant (TAC), and reduced glutathione (GSH) with a marked decrease in myeloperoxidase (MPO) and malondialdehyde (MDA) levels). Likewise, hepatic CAT and SOD activities were significantly improved, and the opposite trend was recorded with hepatic MDA. The highest AVP-supplemented dose (10 g/kg) recorded the highest immune-antioxidant status. Based on the study findings, we highlight the efficacy of AVP as a nutraceutical dietary supplementation for aquaculture to enhance growth, physiological performance, and immune-antioxidant status and as a natural economic antibacterial agent in O. niloticus for sustaining aquaculture. It could be concluded that the dietary supplementation of 10 g AVP/kg enhanced O. niloticus growth, physiological performance, immune-antioxidant status, and resistance against F. columnare.
Keywords: Alchemilla vulgaris; Nile tilapia; bacterial challenge; feed additive; growth performance; immune and antioxidant status.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest is reported by the authors.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Dietary propolis complementation relieves the physiological and growth deterioration induced by Flavobacterium columnare infection in juveniles of common carp (Cyprinus carpio).PLoS One. 2023 Oct 13;18(10):e0292976. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0292976. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37831671 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant, Immunostimulant, and Growth-Promoting Effects of Dietary Annona squamosa Leaf Extract on Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, and Its Tolerance to Thermal Stress and Aeromonas sobria Infection.Animals (Basel). 2023 Feb 19;13(4):746. doi: 10.3390/ani13040746. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36830534 Free PMC article.
-
Acrylamide exposure induces growth retardation, neurotoxicity, stress, and immune/antioxidant disruption in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus): The alleviative effects of Chlorella vulgaris diets.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024 Mar;146:109411. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2024.109411. Epub 2024 Jan 30. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38301813
-
Synergistic Effects Between Dietary Zinc Form Supplementation and Dietary Protein Levels on Performance, Intestinal Functional Topography, Hemato-biochemical Indices, Immune, Oxidative Response, and Associated Gene Expression of Nile Tilapia Oreochromis niloticus.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2022 Jul;200(7):3412-3428. doi: 10.1007/s12011-021-02911-y. Epub 2021 Sep 6. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2022. PMID: 34487300
-
Can Agri-Food Waste Be a Sustainable Alternative in Aquaculture? A Bibliometric and Meta-Analytic Study on Growth Performance, Innate Immune System, and Antioxidant Defenses.Foods. 2022 Jun 24;11(13):1861. doi: 10.3390/foods11131861. Foods. 2022. PMID: 35804678 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of extended dietary supplementation with Santalum album essential oil on hemato-biochemical changes, innate immune response, antioxidant status, and expression of related gene in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus).Fish Physiol Biochem. 2024 Jun;50(3):955-971. doi: 10.1007/s10695-024-01309-6. Epub 2024 Feb 1. Fish Physiol Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38300372
-
Dietary propolis complementation relieves the physiological and growth deterioration induced by Flavobacterium columnare infection in juveniles of common carp (Cyprinus carpio).PLoS One. 2023 Oct 13;18(10):e0292976. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0292976. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37831671 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary tea tree (Melaleucae Aetheroleum) oil fortifies growth, biochemical, immune-antioxidant trait, gene function, tissue reaction, and Aeromonas sobria resistance in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus).BMC Vet Res. 2025 Jan 2;21(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s12917-024-04369-1. BMC Vet Res. 2025. PMID: 39748405 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Dietary Tuber Ethanolic Extract of Nut Grass (Cyperus rotundus Linn.) on Growth, Immune Response, and Disease Resistance in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus).Animals (Basel). 2024 Feb 2;14(3):503. doi: 10.3390/ani14030503. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38338145 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant, Immunostimulant, and Growth-Promoting Effects of Dietary Annona squamosa Leaf Extract on Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, and Its Tolerance to Thermal Stress and Aeromonas sobria Infection.Animals (Basel). 2023 Feb 19;13(4):746. doi: 10.3390/ani13040746. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36830534 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tilami S.K., Sampels S. Nutritional value of fish: Lipids, proteins, vitamins, and minerals. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2018;26:243–253. doi: 10.1080/23308249.2017.1399104. - DOI
-
- Mansour A.T., Ashour M., Alprol A.E., Alsaqufi A.S. Aquatic Plants and Aquatic Animals in the Context of Sustainability: Cultivation Techniques, Integration, and Blue Revolution. Sustainability. 2022;14:3257. doi: 10.3390/su14063257. - DOI
-
- El-Sayed A.-F.M. Tilapia Culture. 2nd ed. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2019.
-
- Tartor Y., Taha M., Mahboub H., El Ghamery M. Yeast species associated with diseased fish: Occurrence, identification, experimental challenges and antifungal susceptibility testing. Aquaculture. 2018;488:134–144. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2018.01.033. - DOI
-
- Rahman A.N.A., Mansour D.A., Abd El-Rahman G.I., Elseddawy N.M., Zaglool A.W., Khamis T., Mahmoud S.F., Mahboub H.H. Imidacloprid toxicity in Clarias gariepinus: Protective role of dietary Hyphaene thebaica against biochemical and histopathological disruption, oxidative stress, immune genes expressions, and Aeromonas sobria infection. Aquaculture. 2022;555:738170. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2022.738170. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

