PD-L1/pS6 in Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs) during Osimertinib Treatment in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
- PMID: 36009440
- PMCID: PMC9405335
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10081893
PD-L1/pS6 in Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs) during Osimertinib Treatment in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
Abstract
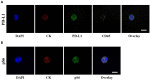
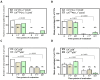
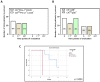
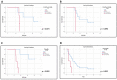
The PD-1/PD-L1 axis provides CTCs an escape route from the immune system. Phosphorylation of the ribosomal protein S6 is implicated in the same pathway, following mTOR activation. The aim of the study was to investigate the expression of PD-L1 and pS6 in CTCs from NSCLC patients under Osimertinib treatment at a single cell level. CTCs were isolated using ISET from NSCLC patients’ blood [37 at baseline, 25 after the 1st cycle, and 23 at the end of treatment (EOT)]. Staining was performed using immunofluorescence. Cytokeratin-positive (CK+) CTCs were detected in 62% of patients. CK+PD-L1+CD45− and CK+pS6+ phenotypes were detected in 38% and 41% of the patients at baseline, in 28% and 32% after 1st cycle, and in 30% and 35% at EOT, respectively. Spearman’s analysis revealed statistically significant correlations between PD-L1 and pS6 phenotypes at all time points. Survival analysis revealed that CK+pS6+ (p = 0.003) and CKlowpS6+ (p = 0.021) phenotypes after 1st cycle were related to significantly decreased one-year progression-free survival (PFS12m) and PFS, respectively. CK+PD-L1+CD45−phenotype at baseline and after 1st cycle showed a trend for decreased PFS12m. Increased expression of PD-L1/pS6 in CTCs of Osimertinib-treated NSCLC patients implies the activation of the corresponding pathway, which is potentially associated with poor clinical outcomes.
Keywords: Osimertinib; PD-L1; circulating tumor cells; non-small cell lung cancer; pS6.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of PD-L1/PD-1 on circulating tumor cells in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2018 Jan 15;10:1758834017750121. doi: 10.1177/1758834017750121. eCollection 2018. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29383038 Free PMC article.
-
Detyrosinated α-Tubulin, Vimentin and PD-L1 in Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs) Isolated from Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Patients.J Pers Med. 2022 Jan 25;12(2):154. doi: 10.3390/jpm12020154. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35207643 Free PMC article.
-
PD-L1 Expression with Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition of Circulating Tumor Cells Is Associated with Poor Survival in Curatively Resected Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Jun 11;11(6):806. doi: 10.3390/cancers11060806. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31212653 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of programmed cell death-ligand 1 expression on circulating tumor cells in various cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Med. 2021 Oct;10(20):7021-7039. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4236. Epub 2021 Aug 23. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 34423578 Free PMC article.
-
Is the Blood an Alternative for Programmed Cell Death Ligand 1 Assessment in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer?Cancers (Basel). 2019 Jun 30;11(7):920. doi: 10.3390/cancers11070920. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31262041 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Circulating Tumour Cells: Detection and Application in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 8;24(22):16085. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216085. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effectiveness comparison of third-generation EGFR-TKI as initial and sequential therapy in adjuvant treatment for EGFR mutation-sensitive stage IIIA non-small cell lung cancer after surgery.Heliyon. 2023 Oct 13;9(11):e20955. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20955. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37920491 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative analysis of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) and exosomes from small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) patients: a comprehensive approach.Mol Oncol. 2025 Jul;19(7):2038-2055. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13765. Epub 2024 Nov 22. Mol Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39575761 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid biopsy for human cancer: cancer screening, monitoring, and treatment.MedComm (2020). 2024 May 28;5(6):e564. doi: 10.1002/mco2.564. eCollection 2024 Jun. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 38807975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive liquid biopsy analysis for monitoring NSCLC patients under second-line osimertinib treatment.Front Oncol. 2024 Oct 21;14:1435537. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1435537. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39497713 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Koh Y., Yagi S., Akamatsu H., Kanai K., Hayata A., Tokudome N., Akamatsu K., Higuchi M., Kanbara H., Nakanishi M., et al. Heterogeneous expression of programmed death receptor-ligand 1 on circulating tumor cells in patients with lung cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer. 2019;20:270–277.e271. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2019.03.004. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gallo M., De Luca A., Maiello M.R., D’Alessio A., Esposito C., Chicchinelli N., Forgione L., Piccirillo M.C., Rocco G., Morabito A., et al. Clinical utility of circulating tumor cells in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2017;6:486–498. doi: 10.21037/tlcr.2017.05.07. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kallergi G., Kontopodis E., Ntzifa A., Jordana-Ariza N., Karachaliou N., Pantazaka E., Charalambous H.A., Psyrri A., Tsaroucha E., Boukovinas I., et al. Effect of osimertinib on CTCs and ctDNA in EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer patients: The prognostic relevance of liquid biopsy. Cancers. 2022;14:1574. doi: 10.3390/cancers14061574. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

