RNA Modifications in Gastrointestinal Cancer: Current Status and Future Perspectives
- PMID: 36009465
- PMCID: PMC9405978
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10081918
RNA Modifications in Gastrointestinal Cancer: Current Status and Future Perspectives
Abstract
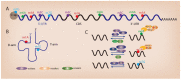
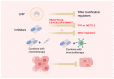
Gastrointestinal (GI) cancer, referring to cancers of the digestive system such as colorectal cancer (CRC), gastric cancer (GC), and liver cancer, is a major cause of cancer-related deaths in the world. A series of genetic, epigenetic, and epitranscriptomic changes occur during the development of GI cancer. The identification of these molecular events provides potential diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic targets for cancer patients. RNA modification is required in the posttranscriptional regulation of RNA metabolism, including splicing, intracellular transport, degradation, and translation. RNA modifications such as N6-methyladenosine (m6A) and N1-methyladenosine (m1A) are dynamically regulated by three different types of regulators named methyltransferases (writers), RNA binding proteins (readers), and demethylases (erasers). Recent studies have pointed out that abnormal RNA modification contributes to GI tumorigenesis and progression. In this review, we summarize the latest findings on the functional significance of RNA modification in GI cancer and discuss the therapeutic potential of epitranscriptomic inhibitors for cancer treatment.
Keywords: RNA modification; gastrointestinal cancer; therapeutic target.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of N6-methyladenosine RNA modification in gastric cancer.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Jul 13;9(1):241. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01485-z. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 37443100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging roles of RNA methylation in gastrointestinal cancers.Cancer Cell Int. 2020 Dec 7;20(1):585. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01679-w. Cancer Cell Int. 2020. PMID: 33372610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA N6-Methyladenine Modification, Cellular Reprogramming, and Cancer Stemness.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jul 4;10:935224. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.935224. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35859892 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress on m6A and drug resistance in gastrointestinal tumors.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 28;16:1565738. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1565738. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40356985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional Impacts of Epitranscriptomic m6A Modification on HIV-1 Infection.Viruses. 2024 Jan 16;16(1):127. doi: 10.3390/v16010127. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38257827 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and functional characterization of m1A-related genes in colorectal cancer: implications for prognosis, immune infiltration, and therapeutic strategies.Front Oncol. 2025 Feb 18;15:1532602. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1532602. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40040720 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of methylation-related genes in diagnosis and subtype classification of renal interstitial fibrosis.Hereditas. 2023 Jul 27;160(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s41065-023-00295-8. Hereditas. 2023. PMID: 37496082 Free PMC article.
-
Epitranscriptome: Review of Top 25 Most-Studied RNA Modifications.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 10;23(22):13851. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213851. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The regulatory role of N6-methyladenosine RNA modification in gastric cancer: Molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets.Front Oncol. 2022 Dec 6;12:1074307. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1074307. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36561529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetically Regulating Non-coding RNAs in Colorectal Cancer: Promises and Potentials.Middle East J Dig Dis. 2025 Jan;17(1):40-53. doi: 10.34172/mejdd.2025.404. Epub 2025 Jan 31. Middle East J Dig Dis. 2025. PMID: 40322568 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

