Polygenic Risk Score Improves Cataract Prediction in East Asian Population
- PMID: 36009466
- PMCID: PMC9406175
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10081920
Polygenic Risk Score Improves Cataract Prediction in East Asian Population
Abstract
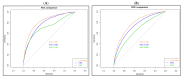
Cataracts, characterized by crystalline lens opacities in human eyes, is the leading cause of blindness globally. Due to its multifactorial complexity, the molecular mechanisms remain poorly understood. Larger cohorts of genome-wide association studies (GWAS) are needed to investigate cataracts’ genetic basis. In this study, a GWAS was performed on the largest Han population to date, analyzing a total of 7079 patients and 13,256 controls from the Taiwan Biobank (TWB) 2.0 cohort. Two cataract-associated SNPs with an adjustment of p < 1 × 10−7 in the older groups and nine SNPs with an adjustment of p < 1 × 10−6 in the younger group were identified. Except for the reported AGMO in animal models, most variations, including rs74774546 in GJA1 and rs237885 in OXTR, were not identified before this study. Furthermore, a polygenic risk score (PRS) was created for the young and old populations to identify high-risk cataract individuals, with areas under the receiver operating curve (AUROCs) of 0.829 and 0.785, respectively, after covariate adjustments. Younger individuals had 17.45 times the risk while older people had 10.97 times the risk when comparing individuals in the highest and lowest PRS quantiles. Validation analysis on an independent TWB1.0 cohort revealed AUROCs of 0.744 and 0.659.
Keywords: Asian population; biobank; cataract; genome-wide association studies; polygenic risk score; retrospective study.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Genome-Wide Polygenic Risk Score for Predicting High Risk Glaucoma Individuals of Han Chinese Ancestry.J Pers Med. 2021 Nov 9;11(11):1169. doi: 10.3390/jpm11111169. J Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 34834521 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analyses identify novel risk loci for cluster headache in Han Chinese residing in Taiwan.J Headache Pain. 2022 Nov 21;23(1):147. doi: 10.1186/s10194-022-01517-6. J Headache Pain. 2022. PMID: 36404298 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of genome-wide polygenic risk scores for predicting breast cancer incidence in Japanese females: a population-based case-cohort study.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2023 Feb;197(3):661-671. doi: 10.1007/s10549-022-06843-6. Epub 2022 Dec 20. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2023. PMID: 36538246
-
A polygenic risk score for breast cancer risk in a Taiwanese population.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2017 May;163(1):131-138. doi: 10.1007/s10549-017-4144-5. Epub 2017 Feb 15. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2017. PMID: 28205043
-
Genome-wide association studies and polygenic risk scores for skin cancer: clinically useful yet?Br J Dermatol. 2019 Dec;181(6):1146-1155. doi: 10.1111/bjd.17917. Epub 2019 Jul 7. Br J Dermatol. 2019. PMID: 30908599 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Saffron's protective role against atherosclerosis-induced cataract progression in New Zealand white rabbits with phytochemical analysis of saffron's extract.PLoS One. 2025 Jan 14;20(1):e0315178. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0315178. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39808674 Free PMC article.
-
Microvascular and macrovascular complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus: Exome wide association analyses.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 23;14:1143067. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1143067. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37033211 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Group E.E.S. Prophylaxis of postoperative endophthalmitis following cataract surgery: Results of the ESCRS multicenter study and identification of risk factors. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2007;33:978–988. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

