Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) in Young Synthetic Cannabinoids Abusers
- PMID: 36009483
- PMCID: PMC9406021
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10081936
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) in Young Synthetic Cannabinoids Abusers
Abstract
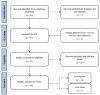
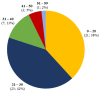
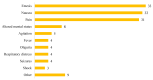
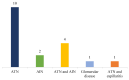
Background. Synthetic cannabinoid-related acute kidney injury represents an increasingly important public health issue due to the diagnostic challenges given by low clinical suspicion of the disease and the frequent undetectability in routine drug tests. Methods. A systematic literature search on PubMed was carried out until 31 January 2022. Case reports, case series, retrospective and prospective studies, as well as reviews on acute kidney injury related to the consumption of synthetic cannabinoid were searched. Results. The systematic review process selected 21 studies for a total of 55 subjects with synthetic cannabinoid-induced acute kidney injury. Renal damage was demonstrated by elevated serum creatinine levels in 49 patients (89%). On renal ultrasound, the most frequent finding was an increase in cortical echogenicity. Renal biopsy, performed in 33% of cases, revealed acute tubular damage, acute tubulointerstitial nephritis, and acute interstitial nephritis, in decreasing order of frequency. Conclusion. Prompt identification and treatment of synthetic cannabinoid-related acute kidney injury represent a sensitive public health goal both for the acute management of damage from synthetic cannabinoids and for the prevention of chronic kidney disease.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; acute tubular damage; intoxication; synthetic cannabinoids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synthetic cannabinoid-associated acute interstitial nephritis: An emerging cause of pediatric acute kidney injury?Clin Nephrol Case Stud. 2023 Mar 27;11:55-60. doi: 10.5414/CNCS111063. eCollection 2023. Clin Nephrol Case Stud. 2023. PMID: 37006641 Free PMC article.
-
Acute kidney injury associated with smoking synthetic cannabinoid.Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2014 Aug;52(7):664-73. doi: 10.3109/15563650.2014.932365. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2014. PMID: 25089722
-
Synthetic Cannabinoid Induced acute Tubulointerstitial Nephritis and Uveitis Syndrome: A Case Report and Review of Literature.J Clin Diagn Res. 2016 May;10(5):OD31-2. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2016/18762.7826. Epub 2016 May 1. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016. PMID: 27437289 Free PMC article.
-
The role of cannabinoid signaling in acute and chronic kidney diseases.Kidney Int. 2018 Aug;94(2):252-258. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2018.01.024. Epub 2018 Apr 27. Kidney Int. 2018. PMID: 29706358 Review.
-
Tubulointerstitial Injury and Drugs of Abuse.Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2017 Mar;24(2):80-85. doi: 10.1053/j.ackd.2016.09.008. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2017. PMID: 28284383 Review.
Cited by
-
Poisoning-Induced Acute Kidney Injury: A Review.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Aug 12;60(8):1302. doi: 10.3390/medicina60081302. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39202583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Renal Outcomes and Other Adverse Effects of Cannabinoid Supplementation.Nutrients. 2024 Dec 27;17(1):59. doi: 10.3390/nu17010059. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39796493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vivo assessment of the nephrotoxic effects of the synthetic cannabinoid AB-FUBINACA.Forensic Toxicol. 2025 Jan;43(1):86-96. doi: 10.1007/s11419-024-00699-9. Epub 2024 Aug 9. Forensic Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39120650 Free PMC article.
-
Chasing Highs, Experiencing Lows: A Case of Hypokalemia Associated With Cannabis Use.Cureus. 2025 Apr 29;17(4):e83194. doi: 10.7759/cureus.83194. eCollection 2025 Apr. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40443614 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Abuse Potential of Three Indazole-Carboxamide Synthetic Cannabinoids 5F-ADB, MDMB-4en-PINACA and ADB-4en-PINACA.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 3;26(13):6409. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136409. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40650186 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

