Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular Diseases: New Insights into Molecular Mechanisms of Atherosclerosis, Arterial Hypertension, and Coronary Artery Disease
- PMID: 36009488
- PMCID: PMC9405799
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10081938
Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular Diseases: New Insights into Molecular Mechanisms of Atherosclerosis, Arterial Hypertension, and Coronary Artery Disease
Abstract
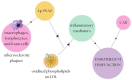
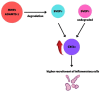
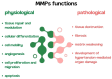
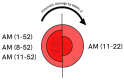
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are disorders associated with the heart and circulatory system. Atherosclerosis is its major underlying cause. CVDs are chronic and can remain hidden for a long time. Moreover, CVDs are the leading cause of global morbidity and mortality, thus creating a major public health concern. This review summarizes the available information on the pathophysiological implications of CVDs, focusing on coronary artery disease along with atherosclerosis as its major cause and arterial hypertension. We discuss the endothelium dysfunction, inflammatory factors, and oxidation associated with atherosclerosis. Mechanisms such as dysfunction of the endothelium and inflammation, which have been identified as critical pathways for development of coronary artery disease, have become easier to diagnose in recent years. Relatively recently, evidence has been found indicating that interactions of the molecular and cellular elements such as matrix metalloproteinases, elements of the immune system, and oxidative stress are involved in the pathophysiology of arterial hypertension. Many studies have revealed several important inflammatory and genetic risk factors associated with CVDs. However, further investigation is crucial to improve our knowledge of CVDs progression and, more importantly, accelerate basic research to improve our understanding of the mechanism of pathophysiology.
Keywords: arterial hypertension; atherosclerosis; cardiovascular disease; coronary artery disease; genetic factor; inflammation; matrix metalloproteinases; oxidative stress; vascular endothelium dysfunction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wong N.D., Budoff M.J., Ferdinand K., Graham I.M., Michos E.D., Reddy T., Shapiro M.D., Toth P.P. Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk assessment: An American Society for Preventive Cardiology clinical practice statement. Am. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2022;10:100335. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpc.2022.100335. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

