Quantitative Measurement of Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid by Cascade Artificial Intelligence Models in Patients with Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
- PMID: 36009595
- PMCID: PMC9405775
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10082049
Quantitative Measurement of Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid by Cascade Artificial Intelligence Models in Patients with Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
Abstract
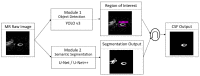
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) hypovolemia is the core of spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH). More than 1000 magnetic resonance myelography (MRM) images are required to evaluate each subject. An effective spinal CSF quantification method is needed. In this study, we proposed a cascade artificial intelligence (AI) model to automatically segment spinal CSF. From January 2014 to December 2019, patients with SIH and 12 healthy volunteers (HVs) were recruited. We evaluated the performance of AI models which combined object detection (YOLO v3) and semantic segmentation (U-net or U-net++). The network of performance was evaluated using intersection over union (IoU). The best AI model was used to quantify spinal CSF in patients. We obtained 25,603 slices of MRM images from 13 patients and 12 HVs. We divided the images into training, validation, and test datasets with a ratio of 4:1:5. The IoU of Cascade YOLO v3 plus U-net++ (0.9374) was the highest. Applying YOLO v3 plus U-net++ to another 13 SIH patients showed a significant decrease in the volume of spinal CSF measured (59.32 ± 10.94 mL) at disease onset compared to during their recovery stage (70.61 ± 15.31 mL). The cascade AI model provided a satisfactory performance with regard to the fully automatic segmentation of spinal CSF from MRM images. The spinal CSF volume obtained through its measurements could reflect a patient's clinical status.
Keywords: CSF segmentation; SIH; cascade AI model; deep learning; object detection; semantic segmentation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Patterns of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) distribution in patients with spontaneous intracranial hypotension: Assessed with magnetic resonance myelography.J Chin Med Assoc. 2017 Feb;80(2):109-116. doi: 10.1016/j.jcma.2016.02.013. Epub 2016 Oct 12. J Chin Med Assoc. 2017. PMID: 27743810
-
Assessing Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leaks in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension With a Scoring System Based on Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings.JAMA Neurol. 2019 May 1;76(5):580-587. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.4921. JAMA Neurol. 2019. PMID: 30776059 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Presentation, Investigation Findings, and Treatment Outcomes of Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA Neurol. 2021 Mar 1;78(3):329-337. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.4799. JAMA Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33393980 Free PMC article.
-
Layered deep learning for automatic mandibular segmentation in cone-beam computed tomography.J Dent. 2021 Nov;114:103786. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2021.103786. Epub 2021 Aug 20. J Dent. 2021. PMID: 34425172
-
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension: updates from diagnosis to treatment.Neuroradiology. 2023 Feb;65(2):233-243. doi: 10.1007/s00234-022-03079-5. Epub 2022 Nov 7. Neuroradiology. 2023. PMID: 36336758 Review.
Cited by
-
Quantification of cervical spinal stenosis by automated 3D MRI segmentation of spinal cord and cerebrospinal fluid space.Spinal Cord. 2024 Jul;62(7):371-377. doi: 10.1038/s41393-024-00993-8. Epub 2024 Apr 16. Spinal Cord. 2024. PMID: 38627568 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying Patients with CSF-Venous Fistula Using Brain MRI: A Deep Learning Approach.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2024 Apr 8;45(4):439-443. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A8173. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2024. PMID: 38423747 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yoo H.M., Kim S.J., Choi C.G., Lee D.H., Lee J.H., Suh D.C., Choi J.W., Jeong K.S., Chung S.J., Kim J.S., et al. Detection of CSF leak in spinal CSF leak syndrome using MR myelography: Correlation with radioisotope cisternography. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2008;29:649–654. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A0920. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen C.H., Chen J.H., Chen H.C., Chai J.W., Chen P.L., Chen C.C. Patterns of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) distribution in patients with spontaneous intracranial hypotension: Assessed with magnetic resonance myelography. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2017;80:109–116. doi: 10.1016/j.jcma.2016.02.013. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources