Schizothorax prenanti Heat Shock Protein 27 Gene: Cloning, Expression, and Comparison with Other Heat Shock Protein Genes after Poly (I:C) Induction
- PMID: 36009624
- PMCID: PMC9404436
- DOI: 10.3390/ani12162034
Schizothorax prenanti Heat Shock Protein 27 Gene: Cloning, Expression, and Comparison with Other Heat Shock Protein Genes after Poly (I:C) Induction
Abstract
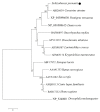
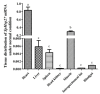
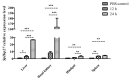
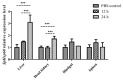
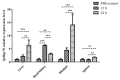
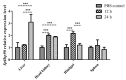
We identified and cloned cDNA encoding the heat shock protein (Hsp) 27 gene from Schizothorax prenanti (SpHsp27), and compared its expression with that of SpHsp60, SpHsp70, and SpHsp90 in the liver, head kidney, hindgut, and spleen of S. prenanti that were injected with polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid [Poly (I:C)]. The SpHsp27 partial cDNA (sequence length, 653 bp; estimated molecular mass, 5.31 kDa; theoretical isoelectric point, 5.09) contained an open reading frame of 636 bp and a gene encoding 211 amino acids. The SpHsp27 amino acid sequence shared 61.0−92.89% identity with Hsp27 sequences from other vertebrates and SpHsp27 was expressed in seven S. prenanti tissues. Poly (I:C) significantly upregulated most SpHsps genes in the tissues at 12 or 24 h (p < 0.05) compared with control fish that were injected with phosphate-buffered saline. However, the intensity of responses of the four SpHsps was organ-specifically increased. The expression of SpHsp27 was increased 163-fold in the head kidney and 26.6-fold SpHsp27 in the liver at 24 h after Poly (I:C) injection. In contrast, SpHsp60 was increased 0.97−1.46-fold in four tissues and SpHsp90 was increased 1.21- and 1.16-fold in the liver and spleen at 12 h after Poly (I:C) injection. Our findings indicated that Poly (I:C) induced SpHsp27, SpHsp60, SpHsp70, and SpHsp90 expression and these organ-specific SpHsps are potentially involved in S. prenanti antiviral immunity or mediate pathological process.
Keywords: Schizothorax prenanti; antiviral immunity; gene expression; heat shock protein 27; polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Molecular characterization and expression analysis of Hsp90 in Schizothorax prenanti.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2016 Nov;21(6):983-991. doi: 10.1007/s12192-016-0723-3. Epub 2016 Aug 15. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2016. PMID: 27527721 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Cloning of Toll-like Receptor 2 and 4 (SpTLR2, 4) and Expression of TLR-Related Genes from Schizothorax prenanti after Poly (I:C) Stimulation.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jul 1;14(7):1388. doi: 10.3390/genes14071388. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37510293 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning of Toll-like Receptor 3 Gene from Schizothorax prenanti (SpTLR3), and Expressions of Seven SpTLRs and SpMyD88 after Lipopolysaccharide Induction.Genes (Basel). 2022 Oct 15;13(10):1862. doi: 10.3390/genes13101862. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36292749 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular cloning and expression of two heat-shock protein genes (HSC70/HSP70) from Prenant's schizothoracin (Schizothorax prenanti).Fish Physiol Biochem. 2015 Apr;41(2):573-85. doi: 10.1007/s10695-015-0030-4. Epub 2015 Feb 18. Fish Physiol Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25690871
-
Molecular cloning, characterization of JunB in Schizothorax prenanti and its roles in responding to Aeromonas hydrophila infection.Int J Biol Macromol. 2020 Dec 1;164:2788-2794. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.08.012. Epub 2020 Aug 4. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020. PMID: 32763408
References
-
- Sørensen J.G., Kristensen T.N., Loeschcke V. The evolutionary and ecological role of heat shock proteins. Ecol. Lett. 2010;6:1025–1037. doi: 10.1046/j.1461-0248.2003.00528.x. - DOI
-
- Ackerman P.A., Forsyth R.B., Mazur C.F., Iwama G.K. Stress hormones and the cellular stress response in salmonids. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2000;23:327–336. doi: 10.1023/A:1011107610971. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

