Detection of Human and Fish Viruses in Marine Gastropods
- PMID: 36009711
- PMCID: PMC9405270
- DOI: 10.3390/ani12162122
Detection of Human and Fish Viruses in Marine Gastropods
Abstract
Marine gastropods represent a major food source for higher trophic levels and an important source of animal protein for humans. Like bivalve molluscs, gastropods can accumulate several types of contaminants; however, the bioaccumulation of microorganisms, particularly viruses, has been poorly investigated in these animals. This study focused on gastropods (Tritia mutabilis, Bolinus brandaris and Rapana venosa) collected during the fishing season from 2017 to 2021 in the north-western Adriatic Sea, and on clams (Ruditapes philippinarum) harvested in the same geographical area, in order to evaluate the presence of human and fish viruses in their tissues. A virological investigation was carried out on the digestive gland using molecular methods. The presence of hepatitis A virus was detected in one sample, whereas noroviruses were not present in the investigated specimens. Regarding fish viruses, it was possible to detect the presence of nervous necrosis virus (NNV) in 26.5% of the analyzed gastropods; however, the histological examination did not show any pathological changes in the nervous tissue in both NNV-positive and -negative batches. As a whole, the investigated gastropods showed the ability to bioaccumulate viruses; however, lower contamination by human viruses compared to bivalve molluscs was pointed out, posing a minor concern to human health.
Keywords: Tritia mutabilis; gastropods; hepatitis A virus; histology; molecular investigation; molluscs; nervous necrosis virus; norovirus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
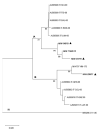
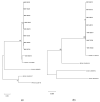
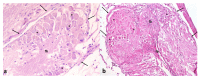
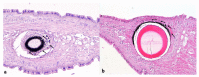
Similar articles
-
Preliminary investigation on the microbiological quality of edible marine gastropods of the Adriatic Sea, Italy.Ital J Food Saf. 2019 Jun 20;8(2):7691. doi: 10.4081/ijfs.2019.7691. eCollection 2019 May 23. Ital J Food Saf. 2019. PMID: 31312618 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial and seasonal variability of human and fish viruses in mussels inside and offshore of Ravenna's harbour (Adriatic Sea, Italy).J Appl Microbiol. 2021 Mar;130(3):994-1008. doi: 10.1111/jam.14806. Epub 2020 Aug 16. J Appl Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 32743895
-
Fate of redspotted grouper nervous necrosis virus (RGNNV) in experimentally challenged Manila clam Ruditapes philippinarum.Dis Aquat Organ. 2017 Jun 19;125(1):53-61. doi: 10.3354/dao03139. Dis Aquat Organ. 2017. PMID: 28627492
-
Shellfish and residual chemical contaminants: hazards, monitoring, and health risk assessment along French coasts.Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2011;213:55-111. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-9860-6_3. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2011. PMID: 21541848 Review.
-
Cockles and mussels, alive, alive, oh-The role of bivalve molluscs as transmission vehicles for human norovirus infections.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2020 Jul;67 Suppl 2:9-25. doi: 10.1111/tbed.13165. Epub 2019 Jun 24. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2020. PMID: 31232515 Review.
Cited by
-
Bacterial Diversity Associated with Terrestrial and Aquatic Snails.Microorganisms. 2024 Dec 24;13(1):8. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13010008. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39858777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Redspotted Grouper Nervous Necrosis Virus and the Reassortant RGNNV/SJNNV In Vitro Susceptibility against a Commercial Peroxy-Acid Biocide under Different Conditions of Use.Vet Sci. 2023 Jan 19;10(2):76. doi: 10.3390/vetsci10020076. Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 36851379 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mallet A., Jouvenel J.-Y., Broyon M., Pirot N., Geffroy B. Histology of Tritia Mutabilis Gonads: Using Reproductive Biology to Support Sustainable Fishery Management. Aquat. Living Resour. 2021;34:6. doi: 10.1051/alr/2021006. - DOI
-
- Serratore P., Ciulli S., Piano A., Cariani A. Shellfish Human Consumption, Health Implication and Conservation Concerns. Nova Science Publishers; New York, NY, USA: 2014. Criticism of the Purication Process of Bivalve Shellfish: Literature Review and Our Industrial Research Experiences; pp. 1–50.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

