Myosin Transducer Inter-Strand Communication Is Critical for Normal ATPase Activity and Myofibril Structure
- PMID: 36009764
- PMCID: PMC9404822
- DOI: 10.3390/biology11081137
Myosin Transducer Inter-Strand Communication Is Critical for Normal ATPase Activity and Myofibril Structure
Abstract
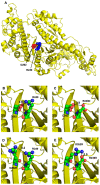
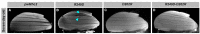
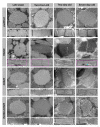
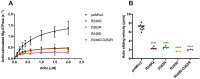
The R249Q mutation in human β-cardiac myosin results in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. We previously showed that inserting this mutation into Drosophila melanogaster indirect flight muscle myosin yields mechanical and locomotory defects. Here, we use transgenic Drosophila mutants to demonstrate that residue R249 serves as a critical communication link within myosin that controls both ATPase activity and myofibril integrity. R249 is located on a β-strand of the central transducer of myosin, and our molecular modeling shows that it interacts via a salt bridge with D262 on the adjacent β-strand. We find that disrupting this interaction via R249Q, R249D or D262R mutations reduces basal and actin-activated ATPase activity, actin in vitro motility and flight muscle function. Further, the R249D mutation dramatically affects myofibril assembly, yielding abnormalities in sarcomere lengths, increased Z-line thickness and split myofibrils. These defects are exacerbated during aging. Re-establishing the β-strand interaction via a R249D/D262R double mutation restores both basal ATPase activity and myofibril assembly, indicating that these properties are dependent upon transducer inter-strand communication. Thus, the transducer plays an important role in myosin function and myofibril architecture.
Keywords: ATPase; Drosophila melanogaster; hypertrophic cardiomyopathy; myofibril; myosin; transducer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

