Impacts of Gut Microbiota on the Immune System and Fecal Microbiota Transplantation as a Re-Emerging Therapy for Autoimmune Diseases
- PMID: 36009962
- PMCID: PMC9404867
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics11081093
Impacts of Gut Microbiota on the Immune System and Fecal Microbiota Transplantation as a Re-Emerging Therapy for Autoimmune Diseases
Abstract
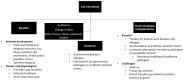
The enormous and diverse population of microorganisms residing in the digestive tracts of humans and animals influence the development, regulation, and function of the immune system. Recently, the understanding of the association between autoimmune diseases and gut microbiota has been improved due to the innovation of high-throughput sequencing technologies with high resolutions. Several studies have reported perturbation of gut microbiota as one of the factors playing a role in the pathogenesis of many diseases, such as inflammatory bowel disease, recurrent diarrhea due to Clostridioides difficile infections. Restoration of healthy gut microbiota by transferring fecal material from a healthy donor to a sick recipient, called fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), has resolved or improved symptoms of autoimmune diseases. This (re)emerging therapy was approved for the treatment of drug-resistant recurrent C. difficile infections in 2013 by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Numerous human and animal studies have demonstrated FMT has the potential as the next generation therapy to control autoimmune and other health problems. Alas, this new therapeutic method has limitations, including the risk of transferring antibiotic-resistant pathogens or transmission of genes from donors to recipients and/or exacerbating the conditions in some patients. Therefore, continued research is needed to elucidate the mechanisms by which gut microbiota is involved in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases and to improve the efficacy and optimize the preparation of FMT for different disease conditions, and to tailor FMT to meet the needs in both humans and animals. The prospect of FMT therapy includes shifting from the current practice of using the whole fecal materials to the more aesthetic transfer of selective microbial consortia assembled in vitro or using their metabolic products.
Keywords: antimicrobial resistance; autoimmune diseases; fecal microbiota transplantation; gut microbiota; hygiene theory; immune system; one health.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rodriguez J.M., Murphy K., Stanton C., Ross R.P., Kober O.I., Juge N., Avershina E., Rudi K., Narbad A., Jenmalm M.C., et al. The composition of the gut microbiota throughout life, with an emphasis on early life. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2015;26:26050. doi: 10.3402/mehd.v26.26050. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

