A Randomized Controlled Trial of Colistin Combined with Sulbactam: 9 g per Day versus 12 g per Day in the Treatment of Extensively Drug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Pneumonia: An Interim Analysis
- PMID: 36009980
- PMCID: PMC9405071
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics11081112
A Randomized Controlled Trial of Colistin Combined with Sulbactam: 9 g per Day versus 12 g per Day in the Treatment of Extensively Drug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Pneumonia: An Interim Analysis
Abstract
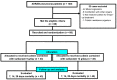
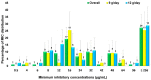
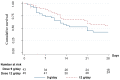
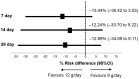
Extensively drug-resistant A. baumannii (XDRAB) pneumonia has a high mortality rate in hospitalized patients. One of the recommended treatments is colistin combined with sulbactam; however, the optimal dosage of sulbactam is unclear. In an open-label, superiority, randomized controlled trial, patients diagnosed with XDRAB pneumonia were randomly assigned (1:1) to receive colistin in combination with sulbactam at either 9 g/day or 12 g/day. The primary outcome was the 28-day mortality rate in the intention-to-treat population. A total of 88 patients received colistin in combination with sulbactam at a dosage of either 12 g/day (n = 45) or 9 g/day (n = 43). Trends toward a lower mortality rate were observed in the 12 g/day group at 7 days (11.1% vs. 23.3%), 14 days (33.3% vs. 41.9%), and 28 days (46.7% vs. 58.1%). The microbiological cure rate at day 7 was significantly higher in the 12 g/day group (90.5% vs. 58.1%; p = 0.02). Factors associated with mortality at 28 days were asthma, cirrhosis, APACHEII score ≥ 28, and a dosage of sulbactam of 9 g/day for mortality at any timepoint. Treatment with colistin combined with sulbactam at 12 g/day was not superior to the combination treatment with sulbactam at 9 g/day. However, due to being an interim analysis, this trial was underpowered to detect mortality differences.
Keywords: A. baumannii XDR pneumonia; colistin; mortality rate; sulbactam.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors received the research drug, sulbactam, from Siam pharmaceutical. CO., LTD. The funding organizations had no role in design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript.
Figures
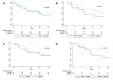
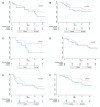
References
-
- Hidron A.I., Edwards J.R., Patel J., Horan T.C., Sievert D.M., Pollock D.A., Fridkin S.K., National Healthcare Safety Network Team. Participating National Healthcare Safety Network Facilities Antimicrobial-resistant pathogens associated with healthcare-associated infections: Annual summary of data reported to the National Healthcare Safety Network at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 2006–2007. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2008;29:996–1011. doi: 10.1086/591861. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jeong B., Na M.J., Son J.W., Jo D.Y., Kwon S.J. High-dose sulbactam treatment for ventilator-associated pneumonia caused by carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Korean J. Crit. Care Med. 2016;31:308–316. doi: 10.4266/kjccm.2015.00703. - DOI
-
- Kasiakou S.K., Michalopoulos A., Soteriades E.S., Samonis G., Sermaides G.J., Falagas M.E. Combination therapy with intravenous colistin for management of infections due to multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria in patients without cystic fibrosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005;49:3136–3146. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.8.3136-3146.2005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

