Identifying Antibiotic Use Targets for the Management of Antibiotic Resistance Using an Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli Case: A Threshold Logistic Modeling Approach
- PMID: 36009985
- PMCID: PMC9405284
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics11081116
Identifying Antibiotic Use Targets for the Management of Antibiotic Resistance Using an Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli Case: A Threshold Logistic Modeling Approach
Abstract
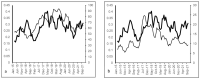
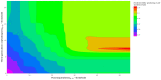
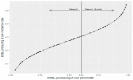
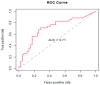
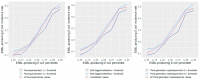
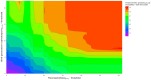
The aim of this study was to develop a logistic modeling concept to improve understanding of the relationship between antibiotic use thresholds and the incidence of resistant pathogens. A combined approach of nonlinear modeling and logistic regression, named threshold logistic, was used to identify thresholds and risk scores in hospital-level antibiotic use associated with hospital-level incidence rates of extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Escherichia coli (E. coli). Threshold logistic models identified thresholds for fluoroquinolones (61.1 DDD/1000 occupied bed days (OBD)) and third-generation cephalosporins (9.2 DDD/1000 OBD) to control hospital ESBL-producing E. coli incidence. The 60th percentile of ESBL-producing E. coli was determined as the cutoff for defining high incidence rates. Threshold logistic analysis showed that for every one-unit increase in fluoroquinolones and third-generation cephalosporins above 61.1 and 9.2 DDD/1000 OBD levels, the average odds of the ESBL-producing E. coli incidence rate being ≥60th percentile of historical levels increased by 4.5% and 12%, respectively. Threshold logistic models estimated the risk scores of exceeding the 60th percentile of a historical ESBL-producing E. coli incidence rate. Threshold logistic models can help hospitals in defining critical levels of antibiotic use and resistant pathogen incidence and provide targets for antibiotic consumption and a near real-time performance monitoring feedback system.
Keywords: ESBL-producing E. coli; antibiotic prescribing; antibiotic resistance; antibiotic stewardship; antibiotic use; clinical practice; epidemiology; threshold logistic modeling; thresholds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aldeyab M.A., López-Lozano J.M., Gould I.M. Global antibiotics use and resistance. In: Babar Z.U.D., editor. Global Pharmaceutical Policy. Palgrave Macmillan; Singapore: 2020. pp. 331–344.
-
- O’Neill J. Antimicrobial Resistance: Tackling a Crisis for the Health and Wealth of Nations. The Review on Antimicrobial Resistance. 2014. [(accessed on 3 June 2022)]. Available online: https://amr-review.org/Publications.html.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

