Benefits of Physical Exercise as Approach to Prevention and Reversion of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children and Adolescents with Obesity
- PMID: 36010064
- PMCID: PMC9406958
- DOI: 10.3390/children9081174
Benefits of Physical Exercise as Approach to Prevention and Reversion of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children and Adolescents with Obesity
Abstract
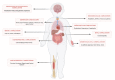
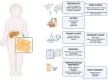
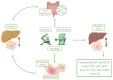
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is an important health concern during childhood; indeed, it is the most frequent cause of chronic liver diseases in obese children. No valid pharmacological therapies for children affected by this condition are available, and the recommended treatment is lifestyle modification, usually including nutrition and exercise interventions. In this narrative review, we summarized up-to-date information on the benefits of physical exercise on NAFLD in children and adolescents with obesity. The role of exercise as non-pharmacological treatment was emphasized in order to provide recent advances on this topic for clinicians not deeply involved in the field. Several studies on obese children and adults confirm the positive role of physical activity (PA) in the treatment of NAFLD, but to date, there are no pediatric randomized clinical trials on exercise versus usual care. Among the pathogenic mechanisms involved in the PA effects on NAFLD, the main players seem to be insulin resistance and related inflammation, oxidative stress, and gut dysbiosis, but further evaluations are necessary to deeply understand whether these factors are correlated and how they synergistically act. Thus, a deeper research on this theme is needed, and it would be extremely interesting.
Keywords: exercise; obesity; pediatrics; physical activity; prevention; steatosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of Dietary and Lifestyle Interventions on Liver, Clinical and Metabolic Parameters in Children and Adolescents with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review.Nutrients. 2020 Sep 19;12(9):2864. doi: 10.3390/nu12092864. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32961669 Free PMC article.
-
Pediatric non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Recent solutions, unresolved issues, and future research directions.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Sep 28;22(36):8078-93. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i36.8078. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27688650 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the Gut Microbiota in Regulating Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children and Adolescents.Front Nutr. 2021 Jun 25;8:700058. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.700058. eCollection 2021. Front Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34250000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lifestyle Interventions Including Nutrition, Exercise, and Supplements for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children.Dig Dis Sci. 2016 May;61(5):1375-86. doi: 10.1007/s10620-016-4126-1. Epub 2016 Apr 4. Dig Dis Sci. 2016. PMID: 27041377 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of physical activity in the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescents.Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2013 Aug;38(8):805-12. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2012-0503. Epub 2013 Apr 29. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2013. PMID: 23855267 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of high-intensity training on fatty infiltration in paraspinal muscles in elderly males with osteosarcopenia - the randomized controlled FrOST study.BMC Geriatr. 2024 Feb 8;24(1):141. doi: 10.1186/s12877-024-04736-5. BMC Geriatr. 2024. PMID: 38326734 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin (SHBG) Reduction: The Alarm Bell for the Risk of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Adolescents with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.Children (Basel). 2022 Nov 15;9(11):1748. doi: 10.3390/children9111748. Children (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36421197 Free PMC article.
-
From Childhood Obesity to Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) and Hyperlipidemia Through Oxidative Stress During Childhood.Metabolites. 2025 Apr 24;15(5):287. doi: 10.3390/metabo15050287. Metabolites. 2025. PMID: 40422865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recompensation in cirrhosis: unravelling the evolving natural history of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jan;21(1):46-56. doi: 10.1038/s41575-023-00846-4. Epub 2023 Oct 5. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 37798441 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

