Sexual-Related Knowledge, School and Family Sexuality Education and Its Association with Experience of Sexual Intercourse among Vocational Secondary School Students in China
- PMID: 36010096
- PMCID: PMC9406409
- DOI: 10.3390/children9081206
Sexual-Related Knowledge, School and Family Sexuality Education and Its Association with Experience of Sexual Intercourse among Vocational Secondary School Students in China
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the associations between sexual-related knowledge, access to school and family sexuality education, and the experience of sexual intercourse, in order to make recommendations on sexuality education for vocational secondary school students in China.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted among 3180 vocational secondary school students in the Shanghai municipality and the Shaanxi province, China. Data were collected through an online, electronic questionnaire, which included socio-demographics, sexual-related knowledge, sources of information, and sexual-related behaviors.
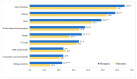
Results: The score on sexual-related knowledge among girls (53.8) is higher than that of boys (48.8), and that of participants from Shanghai (55.2) is higher than their counterparts from Shaanxi (47.6). The proportions of girls (70% and 41.7%, respectively) and participants from Shanghai (65% and 35.7%, respectively) who reported acquiring sexual information from their schools/teachers and parents are higher than that of boys (54.3% and 21.0%, respectively) and their counterparts from Shaanxi (59.7% and 27.4%, respectively). About 6% of participants had experienced sexual intercourse and 10% had watched porn actively. Experience of sexual intercourse was associated with higher sexual-related knowledge scores (OR = 1.01, 95% CI: 1.00-1.02) and active porn watching (OR = 2.63, 95% CI: 1.79-3.84) but was not associated with school and family sexuality education.
Conclusions: Vocational secondary school students had poor sexual knowledge and inadequate school and family sexuality education. School and family-based comprehensive sexuality education should be promoted among vocational secondary school students.
Keywords: China; adolescents; sexual behavior; sexual-related knowledge; sexuality education; vocational secondary school.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Department of Reproductive Health and Research . Adolescent Pregnancy: Evidence Brief. WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2019.
-
- Department of Reproductive Health and Research . Adolescent Sexual and Reproductive Health and Rights. WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2018.
-
- World Health Organization . Global Health Estimates 2015: Deaths by Cause, Age, Sex, by Country and by Region, 2000–2015. WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2016.
-
- Ganchimeg T., Ota E., Morisaki N., Laopaiboon M., Lumbiganon P., Zhang J., Yamdamsuren B., Temmerman M., Say L., Tunçalp Ö., et al. Pregnancy and childbirth outcomes among adolescent mothers: A World Health Organization multicountry study. BJOG. 2014;121((Suppl. 1)):40–48. doi: 10.1111/1471-0528.12630. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources