A Unique Observation of a Patient with Vulto-van Silfhout-de Vries Syndrome
- PMID: 36010237
- PMCID: PMC9406734
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12081887
A Unique Observation of a Patient with Vulto-van Silfhout-de Vries Syndrome
Abstract
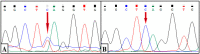
Introduction: Vulto-van Silfhout-de Vries Syndrome (VSVS; OMIM#615828) is a rare hereditary disease associated with impaired intellectual development and speech, delayed psychomotor development, and behavioral anomalies, including autistic behavioral traits and poor eye contact. To date, 27 patients with VSVS have been reported in the literature. Materials and Methods: We describe a 23-year-old male patient with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) who was admitted to the gastroenterological hospital with signs of pseudomembranous colitis. ASD was first noted in the patient at the age of 2.5 years. Later, he developed epileptic seizures and important growth retardation. Prior to the hospitalization, chromosomal aberrations, Fragile X syndrome, and aminoacidopathies/aminoacidurias associated with ASD were excluded. Whole-genome sequencing (WGS) was prescribed to the patient at 23 years old. Results: The patient had a heterozygous carrier of “de novo” variant c.662C > T (p.S221L) in exon 4 of the DEAF1 gene. c.662C > T had not been previously described in genomic databases. According to the ACMG criteria, this missense variant was considered to be pathogenic. VSVS was diagnosed in the patient. Conclusions: The phenotype of the patient is very similar to the data presented in the world literature. However, growth retardation and cachexia, which have not been described previously in the articles, are of interest.
Keywords: DEAF1; VSVS; VULTO-VAN syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Vulto-van Silfhout A.T., Rajamanickam S., Jensik P.J., Vergult S., Rocker N., Newhall K.J., Raghavan R., Reardon S.N., Jarrett K., McIntyre T., et al. Mutations affecting the SAND domain of DEAF1 cause intellectual disability with severe speech impairment and behavioral problems. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2014;94:649–661. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2014.03.013. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vulto-Van Silfhout-De Vries Syndrome VSVS (Online Resource) [(accessed on 26 May 2020)]. Available online: https://www.omim.org/entry/615828.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

