Salivary Gland Toxicity of PSMA-Targeted Radioligand Therapy with 177Lu-PSMA and Combined 225Ac- and 177Lu-Labeled PSMA Ligands (TANDEM-PRLT) in Advanced Prostate Cancer: A Single-Center Systematic Investigation
- PMID: 36010276
- PMCID: PMC9406477
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12081926
Salivary Gland Toxicity of PSMA-Targeted Radioligand Therapy with 177Lu-PSMA and Combined 225Ac- and 177Lu-Labeled PSMA Ligands (TANDEM-PRLT) in Advanced Prostate Cancer: A Single-Center Systematic Investigation
Abstract
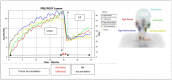
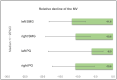
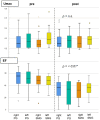
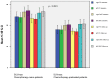
Purpose: PSMA-targeted radioligand therapy (PRLT) is a promising treatment option for patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). However, a high uptake of the radiopharmaceutical in the salivary glands (SG) can lead to xerostomia and becomes dose-limiting for 225Ac-PSMA-617. This study investigated the sialotoxicity of 177Lu-PSMA-I&T/-617 monotherapy and co-administered 225Ac-PSMA-617 and 177Lu-PSMA-617 (Tandem-PPRLT). Methods: Three patient cohorts, that had undergone 177Lu-PSMA-I&T/-617 monotherapy or Tandem-PRLT, were retrospectively analyzed. In a short-term cohort (91 patients), a xerostomia assessment (CTCAE v.5.0), a standardized questionnaire (sXI), salivary gland scintigraphy (SGS), and SG SUVmax and the metabolic volume (MV) on 68Ga-PSMA-11-PET/CT were obtained before and after two cycles of 177Lu-PSMA-I&T/-617. In a long-term cohort, 40 patients were similarly examined. In a Tandem cohort, the same protocol was applied to 18 patients after one cycle of Tandem-PRLT. Results: Grade 1 xerostomia in the short-term follow-up was observed in 22 (24.2%) patients with a worsening of sXI from 7 to 8 at (p < 0.05). In the long-term cohort, xerostomia grades 1 to 2 occurred in 16 (40%) patients. SGS showed no significant changes, but there was a decline of the MV of all SGs. After Tandem-PRLT, 12/18 (66.7%) patients reported xerostomia grades 1 to 2, and the sXI significantly worsened from 9.5 to 14.0 (p = 0.005), with a significant reduction in the excretion fraction (EF) and MV of all SGs. Conclusion: 177Lu-PSMA-I&T/-617 causes only minor SG toxicity, while one cycle of Tandem-PRLT results in a significant SG impairment. This standardized protocol may help to objectify and quantify SG dysfunction.
Keywords: PSMA; mCRPC; radioligand therapy; salivary gland toxicity; xerostomia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
225Ac-PSMA-617/177Lu-PSMA-617 tandem therapy of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: pilot experience.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2020 Mar;47(3):721-728. doi: 10.1007/s00259-019-04612-0. Epub 2019 Nov 22. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2020. PMID: 31758224
-
Therapeutic efficacy, prognostic variables and clinical outcome of 177Lu-PSMA-617 PRLT in progressive mCRPC following multiple lines of treatment: prognostic implications of high FDG uptake on dual tracer PET-CT vis-à-vis Gleason score in such cohort.Br J Radiol. 2019 Dec;92(1104):20190380. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20190380. Epub 2019 Nov 1. Br J Radiol. 2019. PMID: 31600089 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Term Safety and Survival Outcomes of [225Ac]Ac-PSMA (Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen) and [225Ac]Ac-/[177Lu]Lu-PSMA (TANDEM) Radioligand Therapy (PRLT) in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jan 26;17(3):405. doi: 10.3390/cancers17030405. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39941774 Free PMC article.
-
PSMA-targeted radioligand therapy in prostate cancer: current status and future prospects.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2023 Jul-Dec;23(9):959-975. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2023.2247562. Epub 2023 Aug 28. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2023. PMID: 37565281 Review.
-
RadioLigand Therapy with [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 for Salivary Gland Cancers: Literature Review and First Compassionate Use in France.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 May 16;16(5):754. doi: 10.3390/ph16050754. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37242537 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Future Treatment Strategies for Cancer Patients Combining Targeted Alpha Therapy with Pillars of Cancer Treatment: External Beam Radiation Therapy, Checkpoint Inhibition Immunotherapy, Cytostatic Chemotherapy, and Brachytherapy.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Aug 5;17(8):1031. doi: 10.3390/ph17081031. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39204136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiotheranostic landscape: A review of clinical and preclinical development.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2025 Jun;52(7):2685-2709. doi: 10.1007/s00259-025-07103-7. Epub 2025 Feb 1. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2025. PMID: 39891713 Review.
-
Status of PSMA-targeted radioligand therapy in prostate cancer: current data and future trials.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2023 Mar 4;15:17588359231157632. doi: 10.1177/17588359231157632. eCollection 2023. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36895851 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[New tracers and combinations in radioligand therapy for prostate cancer].Urologie. 2023 Jul;62(7):691-695. doi: 10.1007/s00120-023-02125-1. Epub 2023 Jun 15. Urologie. 2023. PMID: 37318583 Review. German.
-
Advancements in PSMA ligand radiolabeling for diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancer: a systematic review.Front Oncol. 2024 Mar 21;14:1373606. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1373606. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38577331 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

